-
Research Article
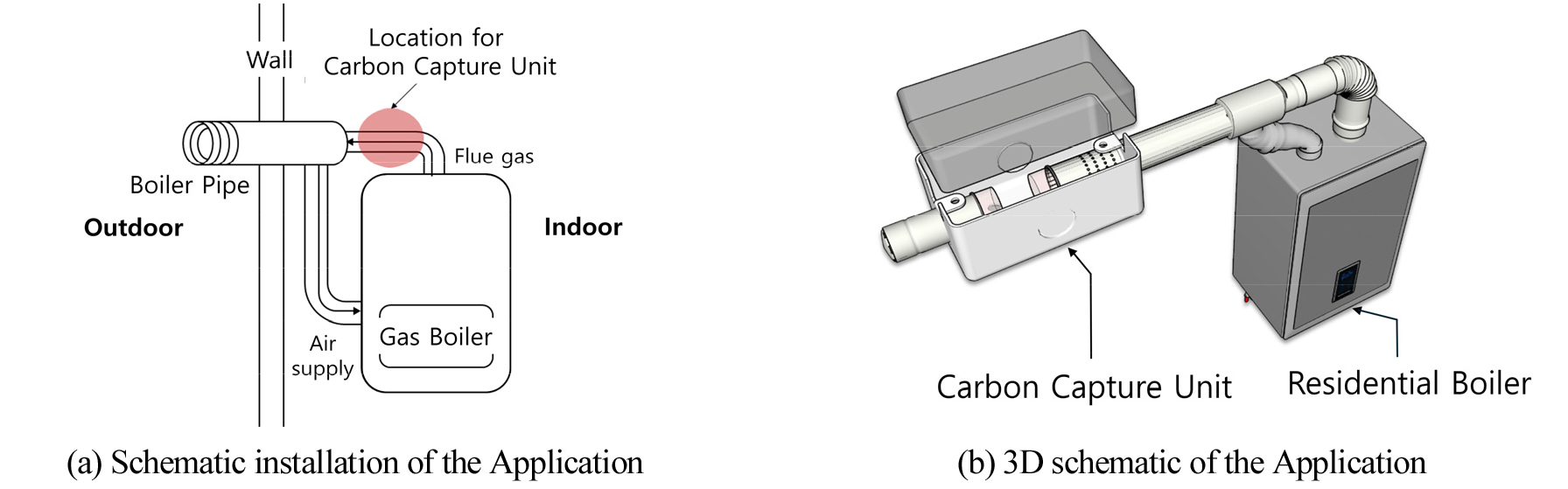
-
A Basic Study on the Application of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) in Domestic Household Boilers
탄소 포집 장치(CCUS)의 가정용 보일러 적용 방안에 대한 기초적 연구
-
Hong Ju-Hyeon, Lee Seung-Le, Son Ji-Won, Kim Jin-Woo, Ryu Seong-Ryong
홍주현, 이승리, 손지원, 김진우, 류성룡
- Given the increasing severity of climate change, we propose a small-scale carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) system applicable to domestic household …
- Given the increasing severity of climate change, we propose a small-scale carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) system applicable to domestic household boilers. The device is designed to be easily attached to existing boiler piping without requiring structural modifications. We conducted experiments using a custom-made acrylic chamber to evaluate the performance of the proposed system in capturing carbon dioxide. The solution with the highest CO₂capture performance was selected through comparative experiments with various absorbent solutions. The results suggest that the proposed CCUS device can reduce direct emissions from residential buildings. This study provides a practical solution to reduce carbon emissions from households and facilitate carbon reuse. - COLLAPSE
-
A Basic Study on the Application of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) in Domestic Household Boilers
-
Research Article
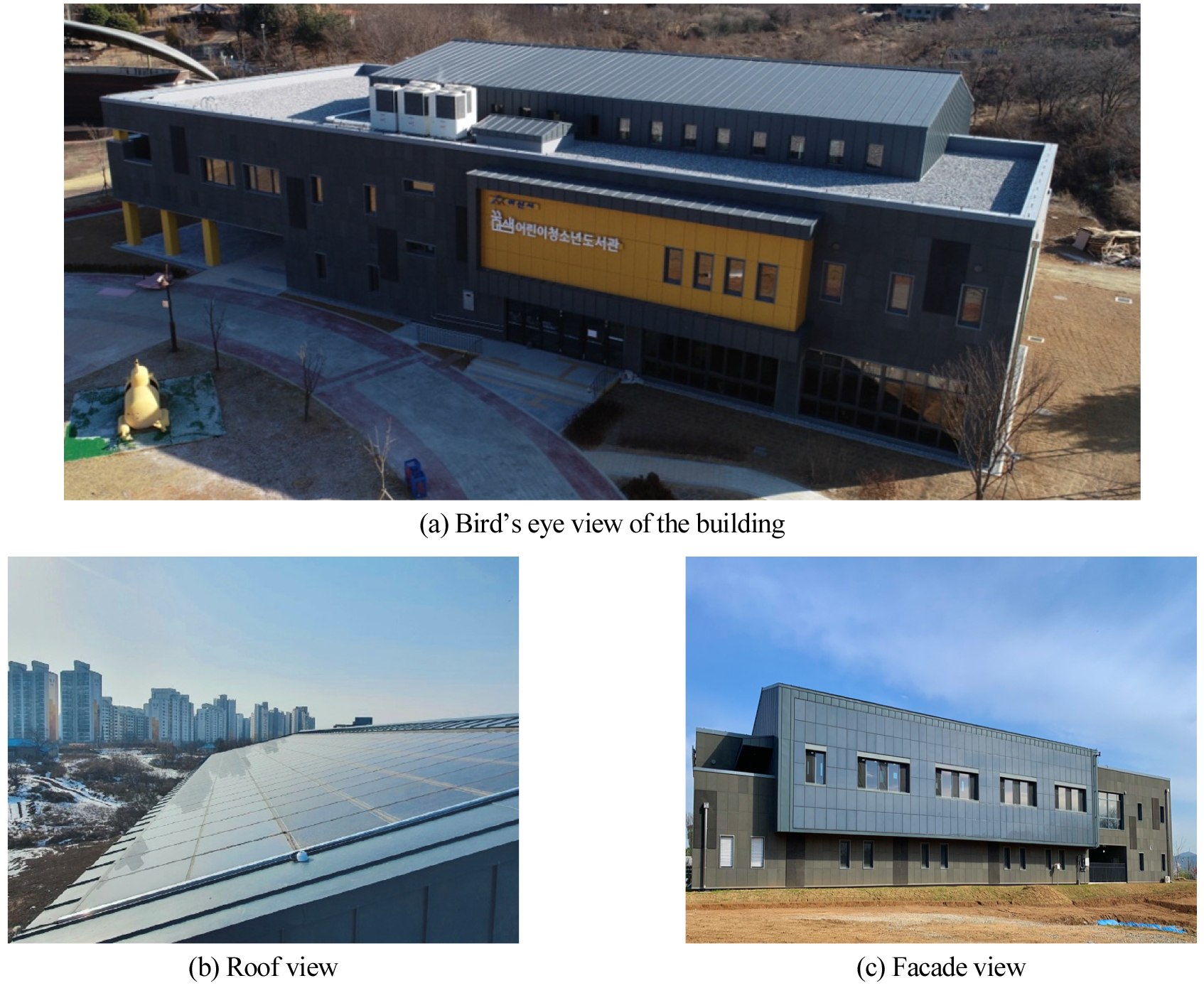

-
Performance Analysis of BIPV System and Power Consumption Modeling with ESS Integration in a Library Building
도서관 건물 적용 BIPV 시스템의 발전성능 및 ESS 연계 전력소비 모델링
-
Lee in-Ho, Kim Sang-Myung, Kim Jin-Hee, Kim Jun-Tae
이인호, 김상명, 김진희, 김준태
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) serve the dual purpose of acting as a building’s façade while simultaneously generating electricity. Although a BIPV system installed …
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) serve the dual purpose of acting as a building’s façade while simultaneously generating electricity. Although a BIPV system installed facing south achieves the maximum power generation at noon on clear days, electrical loads in most buildings occur at varying times throughout the day. When power generation from BIPV systems exceeds the electrical load of a building, surplus electricity is transmitted to the grid managed by the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO). However, if the surplus electricity exceeds the acceptance limit for the grid, power generation from the BIPV system is curtailed. To address this issue, an energy storage system (ESS) must be installed to store surplus electricity and reduce grid load. In this study, we investigated the problem of power curtailment caused by surplus electricity in a library building equipped with a BIPV system. To do so, we used the PVsyst software package to analyze the performance of a BIPV system integrated with an ESS. The results of the analysis indicate that surplus electricity from the BIPV system exceeding the grid acceptance limit necessarily led to power curtailment to maintain a stable grid voltage and frequency. Specifically, we observed that the operation of a simulated BIPV system halted in intervals when surplus power exceeded 7 kWp. To resolve this issue, we integrated an ESS in the simulation that was able to store all the surplus electricity and utilize it within the building instead of feeding the power back into the grid. This approach enabled the building to meet its entire power demand solely from BIPV-generated electricity for up to 7 hours. Consequently, approximately 57% of the library's 13-hour daily operation could be supported by self-generated power. Thus, our results confirm that integrating an ESS with BIPV systems may be expected to enhance the stability of the grid and increase the amount of energy a building can save. Ultimately, the findings underscore the necessity of integrating an ESS with BIPV systems to save electricity and improve energy efficiency. Eventually, the systems could be developed further to realize buildings with zero net energy consumption from the grid. - COLLAPSE
-
Performance Analysis of BIPV System and Power Consumption Modeling with ESS Integration in a Library Building
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Essential Factors in Deep Learning-based Prediction of Cooling Load and Surface Temperature
딥러닝 기반 냉방 부하 및 표면 온도 예측을 위한 주요인자 분석
-
Lee Dong Kyu, Chung Woong June, Park Se Eun
이동규, 정웅준, 박세은
- Radiant floor heating systems ensure a uniform thermal distribution indoors and can provide better thermal comfort to occupants compared to convection systems. …
- Radiant floor heating systems ensure a uniform thermal distribution indoors and can provide better thermal comfort to occupants compared to convection systems. In Korea’s hot and humid climate, however, the use of radiant cooling systems involves some risks of condensation and overcooling. Integrated prediction of building load and surface temperature is essential to resolve these problems. Although various sensors are required for an integrated prediction, an excessive number of sensors can also reduce the practical applicability of a model. To enhance the applicability of predictions, we identified essential input variables to predict building loads and surface temperatures using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), which is one of the most accurate eXplainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Essential Factors in Deep Learning-based Prediction of Cooling Load and Surface Temperature
-
Research Article
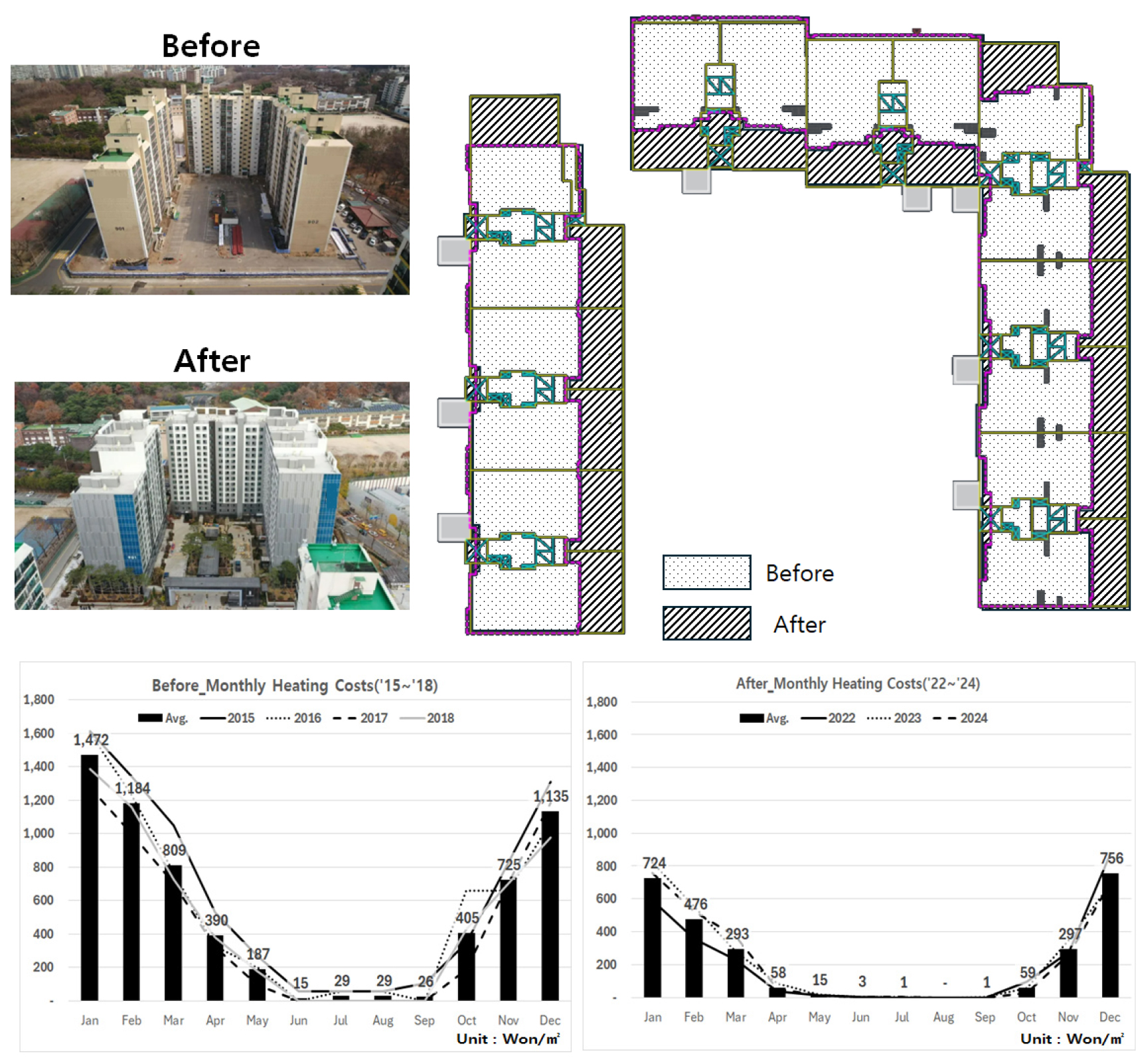
-
A Study on Heating Energy Reduction through Apartment Remodeling and Securing Energy Self-Sufficiency Ratio through Photovoltaic Installation
공동주택 리모델링을 통한 난방에너지 절감과 태양광 설치를 통한 에너지 자립률 확보 연구
-
Kim Seokhyun, Oh Haerin, Cho Hyun, Yoon Suwon
김석현, 오혜린, 조현, 윤수원
- In this study, we analyzed reductions in heating costs in remodeled apartments in terms of maintenance fees due to the difficulty in …
- In this study, we analyzed reductions in heating costs in remodeled apartments in terms of maintenance fees due to the difficulty in quantitatively assessing the effects of remodeling in aging apartment buildings. A comparison of the heating energy consumption of a subject apartment before and after remodeling showed a reduction of approximately 66.8% per unit area. After accounting for an increase in the floor area due to expansion, the reduction per household was approximately 57.8%. An analysis of the proportion of heating costs within total management fees revealed a decrease of approximately 57.5% after the remodeling. A simulation review using the Zero Energy Building (ZEB) certification system revealed that the remodeled building’s primary energy consumption was 119.0 kWh/m2, which achieved ZEB Grade 5 with an energy self-sufficiency rate of 20.94%. These findings confirm that remodeled apartment buildings provide a favorable environment for achieving energy self-sufficiency through rooftop photovoltaic installation. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Heating Energy Reduction through Apartment Remodeling and Securing Energy Self-Sufficiency Ratio through Photovoltaic Installation
-
Research Article
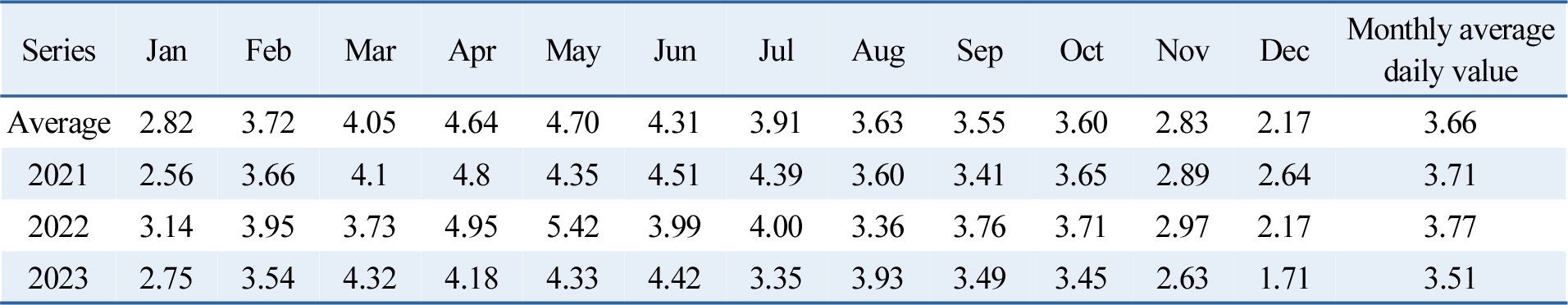
-
A Study on the Appropriate Direct PPA Pricing Compared to KEPCO Tariff for RE100 Implementation
RE100 이행을 위한 한국전력공사 요금제 대비 적정 직접 PPA 단가 산정 연구
-
Kang Heehwan, Hwang Chanhyek, In Byungjoo
강희환, 황찬혁, 인병주
- In this study, we estimate the cost-parity energy price and the internal rate of return (IRR) when replacing Korea Electric Power Corporation …
- In this study, we estimate the cost-parity energy price and the internal rate of return (IRR) when replacing Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) retail tariffs with direct power purchase agreements (direct PPA) amid the expansion of RE100 requirements and rising electricity prices. Methodologically, we defined the peak solar generation window using nationwide average daily solar hours and solar noon time. We then matched KEPCO time-of-use (TOU) rates with the type of day and derived final payable amounts by incorporating the full cost items of ON- and OFF-SITE direct PPAs. Finally, we evaluated 20- and 25-year IRRs. The results show that for industrial (B) high-voltage systems, the ON-SITE cost-parity price of KRW at 192 / kWh yielded IRRs of 13.57% (20-year) and 14.15% (25-year). Furthermore, seven of the nine industrial (B) tariffs have cost-parity prices above the RPS fixed-price cap (KRW 156 / kWh). ON-SITE outperformed OFF-SITE in profitability and substituting industrial (B) tariffs with direct PPAs was economically more favorable than substituting General (B) tariffs. This study provides practical benchmarks and targets for direct PPA design by local governments and corporate RE100 procurement. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Appropriate Direct PPA Pricing Compared to KEPCO Tariff for RE100 Implementation
-
Review
-
A Perspective on Floating and Underwater Photovoltaics: Expanding from FPV to UWPV
수상·수중 태양광 발전 기술 전망: FPV에서 UWPV로의 확장 가능성
-
Ko Seongjin, Cho Seunghee, Lee Junghyun, Kim Joondong
고성진, 조승희, 이정현, 김준동
- This study examined the technological trends and commercialization potential of Floating Photovoltaics (FPVs) and Underwater Photovoltaics (UWPVs) as alternatives to overcoming the …
- This study examined the technological trends and commercialization potential of Floating Photovoltaics (FPVs) and Underwater Photovoltaics (UWPVs) as alternatives to overcoming the site limitations of ground-mounted PVs. FPVs were classified based on their installation environment, with recent commercialization and large-scale deployment cases illustrating both their rapid growth and inherent constraints. UWPVs, optimized for the spectral characteristics of underwater light, could reduce reflection losses and maximize cooling benefits. In addition, recent studies have proposed (1) a modified crystalline silicon cell with bifacial transparent electrodes and a micro-textured SiNₓ antireflection coating, as well as (2) a wide-bandgap metal–oxide–based p–p–n thin-film structure. These designs enhance short-wavelength absorption, improve scattered-light reabsorption, minimize visual impacts, and increase durability under submerged conditions. This study highlights the technical potential of UWPVs, outlines the challenges to commercialization, and underscores the potential of FPV–UWPV integration for expanding renewable-energy generation. - COLLAPSE
-
A Perspective on Floating and Underwater Photovoltaics: Expanding from FPV to UWPV
-
Research Article
-
Rapid Synthesis of Si3N4 via a Two-Step Direct Nitridation Reaction Using Silicon Recycled from End-of-Life Photovoltaic (EoL PV) Modules
태양광 폐모듈로부터 회수한 실리콘의 2단계 직접 질화 반응을 통한 Si3N4 급속 합성
-
Lee Seong-Pyo, Shin Woo-Gyun, Ko Suk-whan, Hwang Hye-mi, Ju Young-chul, Yeo Jeong-Gu, Heo So-Yeon, Kang Gi-hwan, Chang Hyo-Sik, Lee Jin-Seok
이성표, 신우균, 고석환, 황혜미, 주영철, 여정구, 허소연, 강기환, 장효식, 이진석
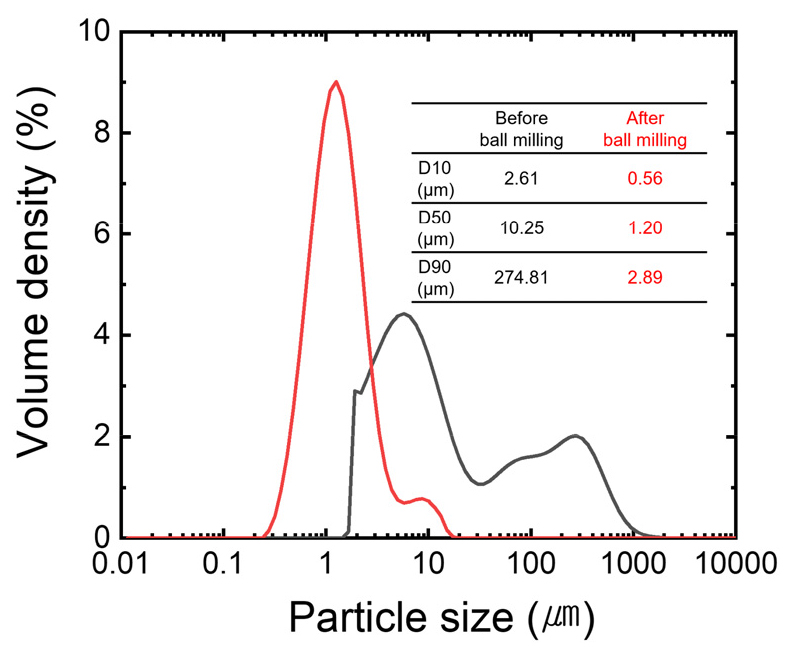
- In this study, recycled Si (r-Si) recovered from end-of-life photovoltaic (EoL PV) modules was used to synthesize Si3N …
- In this study, recycled Si (r-Si) recovered from end-of-life photovoltaic (EoL PV) modules was used to synthesize Si3N4. The recovered r-Si powder was treated via ball milling to obtain an average particle size of approximately 1 µm, after which it was subjected to two-step direct nitridation under a N2–H2 atmosphere. Specifically, first-step nitridation (conducted at 1350℃), which promoted surface nitridation, was followed by second-step nitridation (performed at 1450℃), which enabled complete conversion within 10 min. The resulting Si3N4 predominantly comprised the α-phase (87-91%), and the minor β-phase fraction (9-13%) was attributed to local heat-concentration-induced melting. Additionally, volatile SiO species, generated via the reduction of SiO2 or partial oxidation of Si, reacted with N2 in the gas phase, further contributing to β-Si3N4 formation. Analysis of particle sizes, along with scanning electron microscopy, confirmed grain coarsening at a prolonged holding time. The sample maintained at 1350℃ for 60 min, followed by 10 min at 1450℃ (#60-10), exhibited a smaller particle size with a short processing time, thus representing the optimal synthetic condition. In addition, the mechanism of phase formation was analyzed in terms of the overall two-step nitridation process and the reactions at each temperature. The findings experimentally validate the viability of utilizing r-Si derived from PV modules as a raw material for producing advanced ceramics, contributing to resource circulation and domestic material self-sufficiency. - COLLAPSE
-
Rapid Synthesis of Si3N4 via a Two-Step Direct Nitridation Reaction Using Silicon Recycled from End-of-Life Photovoltaic (EoL PV) Modules
-
Research Article
-
Performance Evaluation of a Natural Solar Lighting and LED Hybrid Louver Window System for Energy Saving in Indoor Vertical Farm
식물공장의 조명 전력에너지 절감을 위한 태양광 LED 하이브리드 루버 외피기술 성능 평가
-
An Youngsub, Kien Ngoc Mihn, Joo Hong-Jin, Lee Kyoung-Ho, Lee Hyun-Hee, Shin Seoyong, Kang Sae-Byul
안영섭, KienNgoc Mihn, 주홍진, 이경호, 이현희, 신서용, 강새별
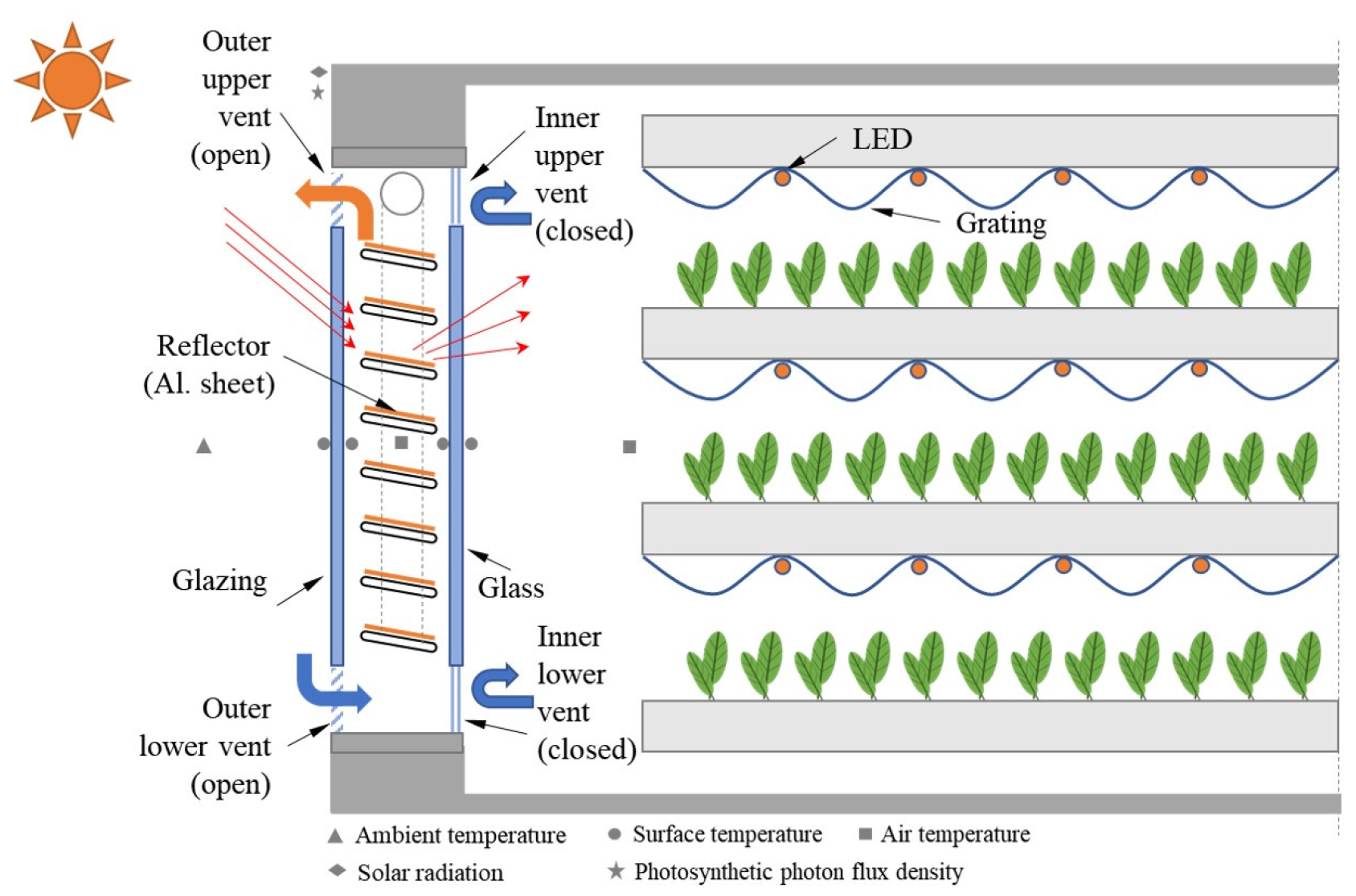
- This study developed a hybrid louver window system (HLWS) that integrates natural solar lighting with light-emitting diode (LED) lighting to reduce the …
- This study developed a hybrid louver window system (HLWS) that integrates natural solar lighting with light-emitting diode (LED) lighting to reduce the electrical energy consumption in an indoor vertical farm. The proposed system enables the required photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) for plant growth through a combination of natural solar and LED lighting. The HLWS is a south-facing louver structure developed to increase natural solar light transmittance and has measurements of 890 (w) × 1,600 (h) mm. Because the intensity of natural solar lighting varies significantly with weather conditions, dimming control of the LED is employed to maintain the target PPFD level required by the plants. Consequently, when applying the HLWS to an indoor vertical farm, the system first maximizes the utilization of available natural solar lighting and then compensates the remaining PPFD deficit through adjustable LED output. The performance of the developed HLWS was evaluated through experimental verification using a full-scale mock-up facility, and numerical simulations were conducted using LightTools software. The results confirmed the PPFD distribution characteristics of the hybrid system combining natural solar lighting and LED and demonstrated the potential of the HLWS to reduce electrical energy consumption by up to 11% in an indoor vertical farm by effectively utilizing natural solar lighting. - COLLAPSE
-
Performance Evaluation of a Natural Solar Lighting and LED Hybrid Louver Window System for Energy Saving in Indoor Vertical Farm
-
Corrigendum
-
CORRIGENDUM to: Numerical Simulation-Based Analysis of Fire Spread Performance in BIPV Cladding Systems
시뮬레이션을 통한 BIPV 클래딩 시스템의 화재 확산 성능 분석
-
Jeong Subin, Kim Jinhee, Kim Juntae
정수빈, 김진희, 김준태
-
CORRIGENDUM to: Numerical Simulation-Based Analysis of Fire Spread Performance in BIPV Cladding Systems
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society











