-
Research Article
-
Experimental Analysis of Power Generation Performance of BIPV Mock-up Systems Considering Color and Thermal Insulation Conditions
건물형 태양광 실증(Mock-up)을 통한 색상 및 단열재 적용에 따른 발전 성능 비교 분석
-
Ryu Eui-Hwan, Kim Kyu-Jin, Kim Deok-Sung, Jeong Jeong-Ho, Kim Min-Je, Choi Jung-Jin, Lee Seung-Joon
류의환, 김규진, 김덕성, 정정호, 김민제, 최정진, 이승준
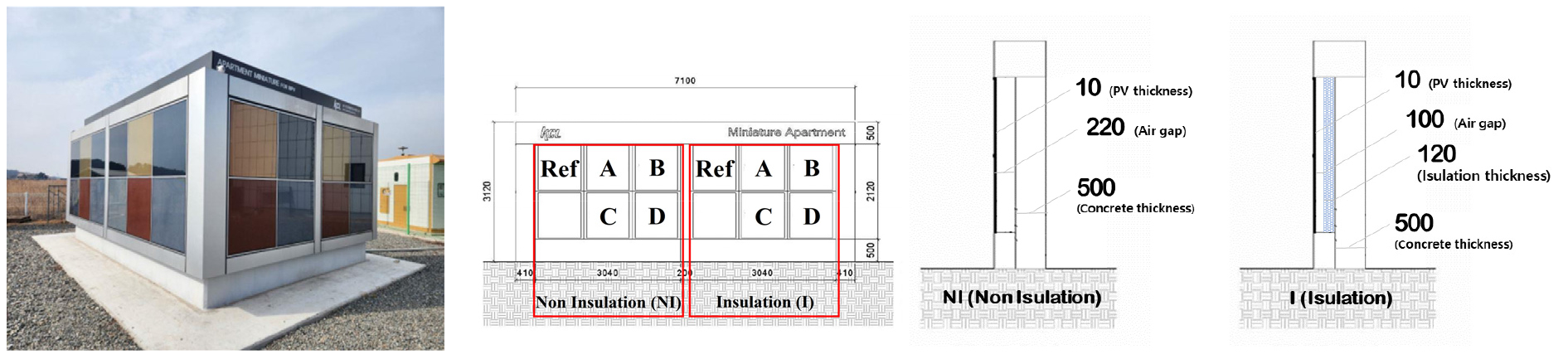
- The effects of color coating and insulation on the power generation performance of building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) systems were experimentally analyzed. A mock-up …
- The effects of color coating and insulation on the power generation performance of building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) systems were experimentally analyzed. A mock-up test bed was constructed, and the irradiance and power generation were measured for one year using south-facing modules. The analysis included colorless (reference), red (Color A), and dark blue (Color B) modules under both insulation (I) and noninsulation (NI) conditions. The output of the Color B module was higher than that of Color A owing to the higher light absorption efficiency of the shorter blue wavelengths. Under insulation conditions, the performance ratio (PR) of Color A was lower by –12% to –24% and that of Color B was lower by –2% to –10% than that of the reference, mainly owing to heat accumulation from suppressed rear heat dissipation. The power generated by BIPV modules is strongly influenced by building envelope factors, such as the coating color and insulation structure. - COLLAPSE
-
Experimental Analysis of Power Generation Performance of BIPV Mock-up Systems Considering Color and Thermal Insulation Conditions
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Convective Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics with Various Installation Conditions of a Quarter-Circle Obstacle in an Air-Based Solar Collector
공기식 태양열 집열기 내 사분원 저항체 설치 조건에 따른 대류 열전달 및 압력강하 특성 분석
-
Jeong Hyeonseok, An Geonyong, Choi Taehwan, Moon Kwangam, An Byeonghwa, Choi Hwiung
정현석, 안건용, 최태환, 문광암, 안병화, 최휘웅
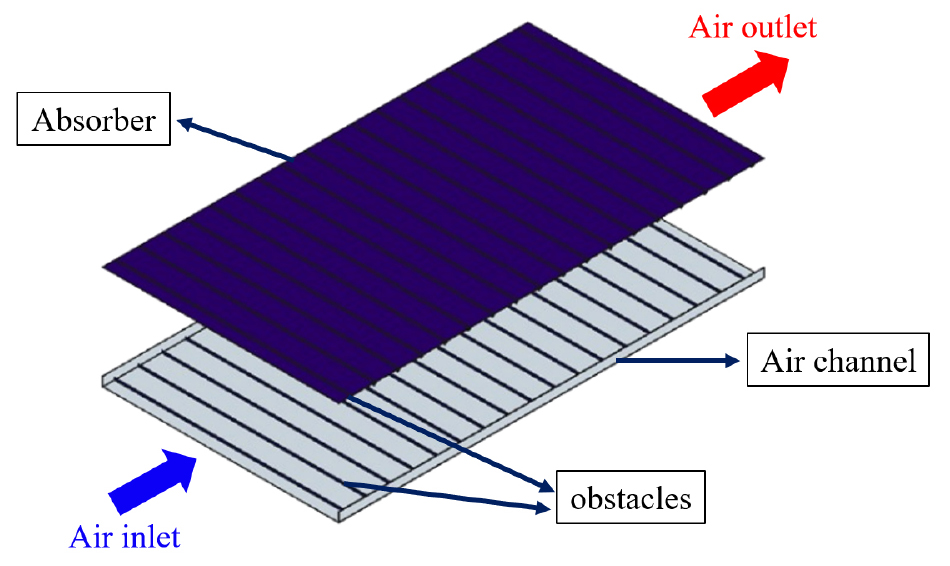
- Air-based solar collectors are renewable systems that produce heated air using solar thermal energy. However, the thermal efficiency of these systems must …
- Air-based solar collectors are renewable systems that produce heated air using solar thermal energy. However, the thermal efficiency of these systems must be increased because of the low thermal conductivity of air. In this study, the heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of a developed air-based solar collector with quarter-circle-shaped obstacles on the upper and lower surfaces of an air channel were investigated. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) was used to analyze the effects of the obstacle installation conditions on the heat transfer and pressure drop. The quarter-circle-shaped obstacle produced a 2.53-fold increase in heat transfer; however, the friction factor also increased 41.38 times. Therefore, the performance factor, which considers heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop, was also evaluated. The performance factor was highest at a Reynolds number of 3000 with installation conditions of e/H = 0.10 and P/e = 40, yielding a value of 1.16. Furthermore, empirical correlations for the Nusselt number and friction factor were developed based on the Reynolds number and obstacle installation conditions. The average absolute percentage errors between the CFD results and the from the correlations were 2.98% and 7.5%, respectively, indicating high agreement between the values. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Convective Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop Characteristics with Various Installation Conditions of a Quarter-Circle Obstacle in an Air-Based Solar Collector
-
Research Article
-
Fault Diagnosis of Photovoltaic Arrays using Inverter Data and Classification Models
인버터 데이터와 분류 모델을 이용한 태양광 어레이 고장진단
-
Shin Woogyun, Ju Youngchul, Hwang Hyemi, Lee Jinsuk, Kwon Youngseo, Kim Changjoon, Ko Sukwhan
신우균, 주영철, 황혜미, 이진석, 권영서, 김창준, 고석환
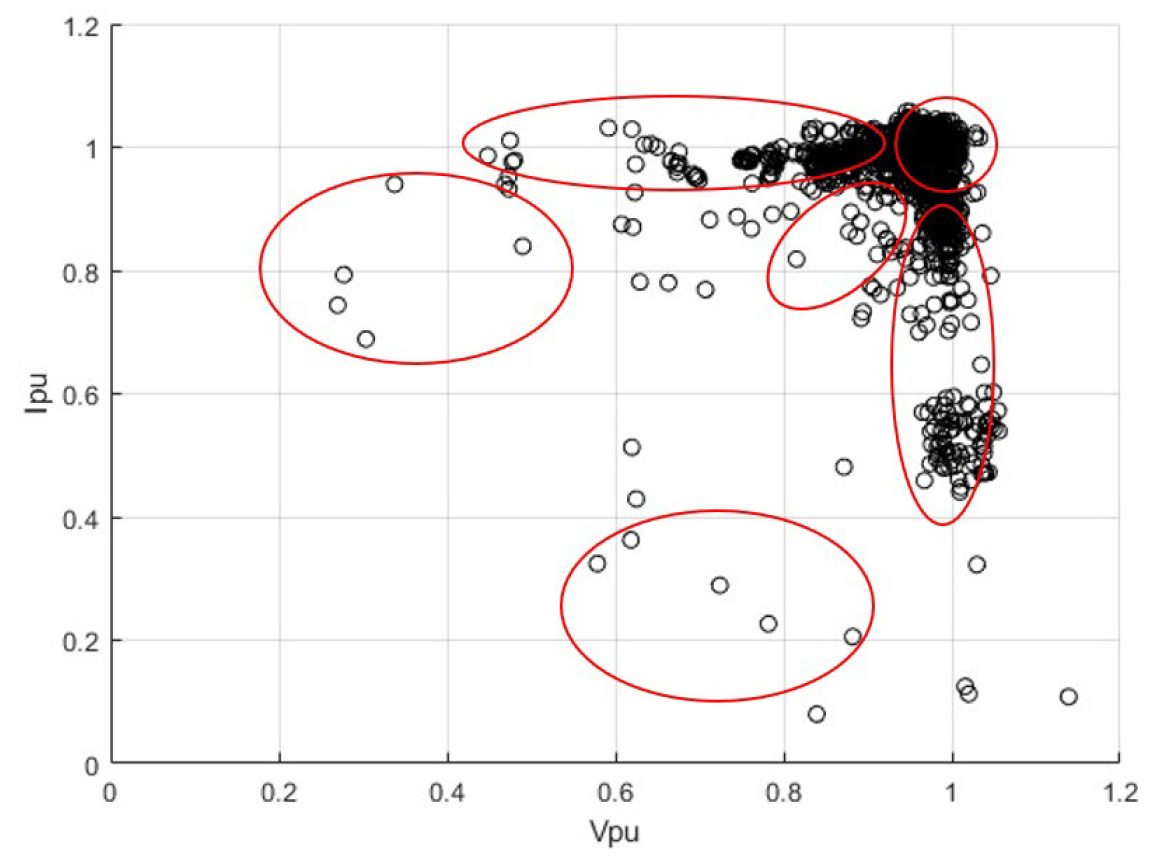
- The expanding deployment of photovoltaic (PV) systems is increasing the demand for diagnostic technologies that accurately assess plant performance and identify faults. …
- The expanding deployment of photovoltaic (PV) systems is increasing the demand for diagnostic technologies that accurately assess plant performance and identify faults. In Korea, the limited availability of areas for installing these technologies has led to the growing adoption of PV systems that vary with site, where access for operation and maintenance (O&M) personnel is often restricted. Data-driven and AI-based diagnostic technologies have been studied, but most research has focused on predicting power output. The accuracy of fault diagnosis can be increased by inferring voltage and current characteristics. In this study, a method for diagnosing the faults of DC PV arrays was developed using inverter-collected data and classification models. Normal and faulty conditions were discriminated by estimating the normal operating state using a regression model based on a previously developed mathematical model. The classification model was trained using a dataset consisting of approximately 1,800 I–V curves at their maximum power points and additional data obtained from simulated fault experiments. Five classification models were evaluated, and the validation accuracy of the k-nearest neighbor (KNN) model was the highest, at 99.8%. The trained KNN model was tested with data collected from two simulated fault types, achieving an average classification accuracy of 98.25%. The proposed diagnostic method more accurately and reliably detects faults in PV power plants and could contribute to increasing the efficiency of O&M activities. - COLLAPSE
-
Fault Diagnosis of Photovoltaic Arrays using Inverter Data and Classification Models
-
Research Article
-
Polymer-free Multilayer Visibly Transparent Radiative Cooler via Spectrally Selective Inverse Design
분광 선택적 역설계를 통한 무고분자 다층 투명 복사 냉각기
-
Lee Daejong, Baek Chansoo
이대종, 백찬수
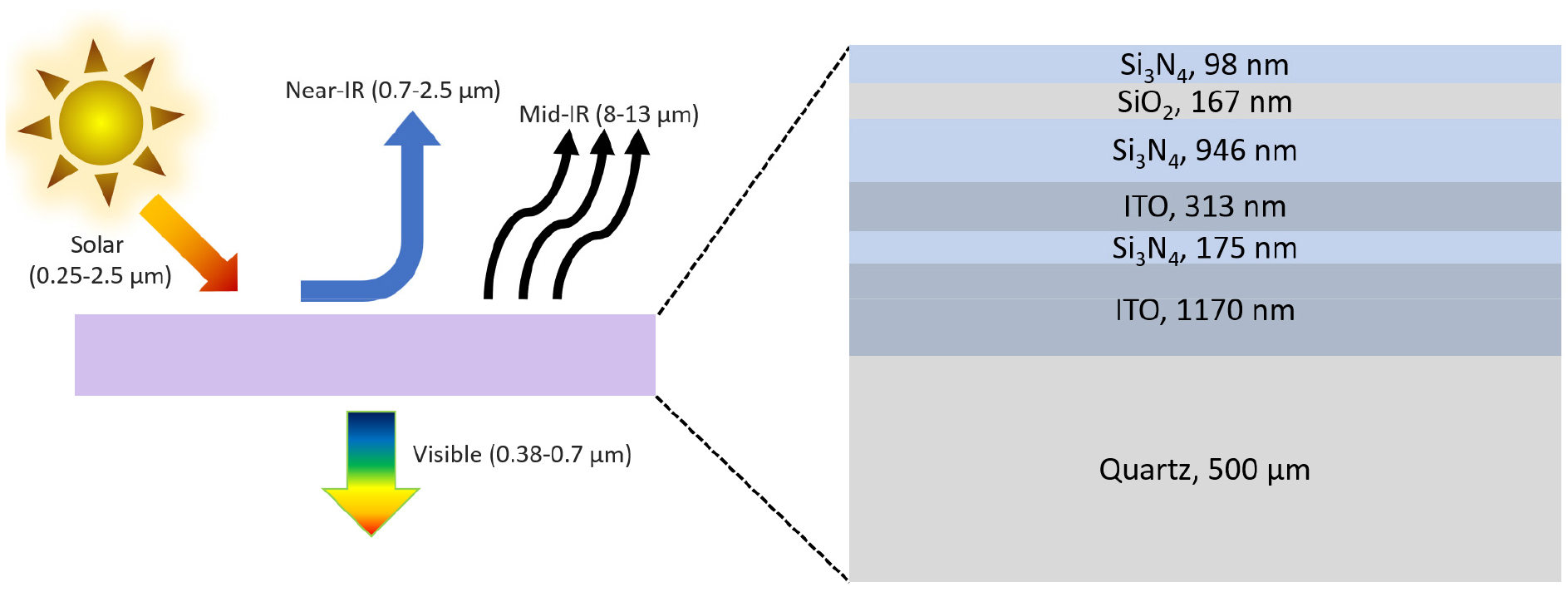
- Radiative cooling is a promising approach for sustainable thermal management that does not consume energy. We developed a polymer-free, multilayer, visibly transparent …
- Radiative cooling is a promising approach for sustainable thermal management that does not consume energy. We developed a polymer-free, multilayer, visibly transparent radiative cooler (PF-MTRC) structure. We designed this structure using a spectrally selective inverse design method based on particle swarm, and we evaluated the performance of the structure through numerical simulations. The visible light transparency, near-infrared reflectance, and mid-infrared absorptivity of a single six-layer PF-MTRC structure were 58.7%, 74.7%, and of 84%, respectively. The solar reflectance and the mid-infrared emissivity of the PF-MTRC were higher than and comparable to those of the conventional polymer-based emitter layer, respectively, demonstrating higher spectral selectivity within a single multilayer design. Additionally, the PF-MTRC was highly stable in the tolerance to thickness variations during fabrication. PF-MTRC shows the potential to overcome the durability issues of conventional polymer-based structures for applications in transparent passive cooling devices. - COLLAPSE
-
Polymer-free Multilayer Visibly Transparent Radiative Cooler via Spectrally Selective Inverse Design
-
Research Article

-
Performance Analysis of PV Systems Applied to Industrial Complex
산업단지 적용 태양광 발전 시스템 성능 분석
-
Oh Wonwook, Choi Jinho
오원욱, 최진호
- The government recently announced various policies to foster RE100 industrial complexes, with the goal of building more than 6 GW of solar …
- The government recently announced various policies to foster RE100 industrial complexes, with the goal of building more than 6 GW of solar power generation systems in these complexes by 2030. Industrial complex solar power generation utilizes idle spaces within industrial complexes, such as factory rooftops and parking lots, for installation of solar power systems. This study analyzed the performance of nine 3 MW solar power plants installed in the Cheongju Industrial Complex as part of the energy self-sufficiency infrastructure development project. All of the plants were installed with bifacial solar modules and exhibited high PR values. A one-year PR analysis confirmed stable operation. Differences in PR values were due to the bifacial gain associated with backlighting. Closely positioned solar panels on east-west-facing factory roofs offer the advantages of increased installation capacity, reduced partial shading, and peak dispersion to mitigate duck curves. From the perspective of utilizing solar power systems, the need to address grid strain and resident acceptance are driving growing interest in industrial complex solar power. However, it is necessary to reflect certain technologies and policies, such as various standard models to increase the participation of factory owners, an east-west power system to resolve future ESS-linked duck curves, and safety management measures for factory roof leaks and fires. - COLLAPSE
-
Performance Analysis of PV Systems Applied to Industrial Complex
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Energy Self-Consumption Ratio and Self-Sufficiency Ratio in PV-ESS Integrated Systems for Industrial Park RE100
산업단지 RE100을 위한 PV-ESS 연계 시스템의 에너지 자가 소비율 및 자립율 분석
-
An Youngsub, Kim Beom-Joo, Jeon Byung-Ki, Kim Min-Hwi, Joo Hong-Jin, Hwang Hye-Mi, Kim Dae-Hwan, Kim Jongkyu
안영섭, 김범주, 전병기, 김민휘, 주홍진, 황혜미, 김대환, 김종규
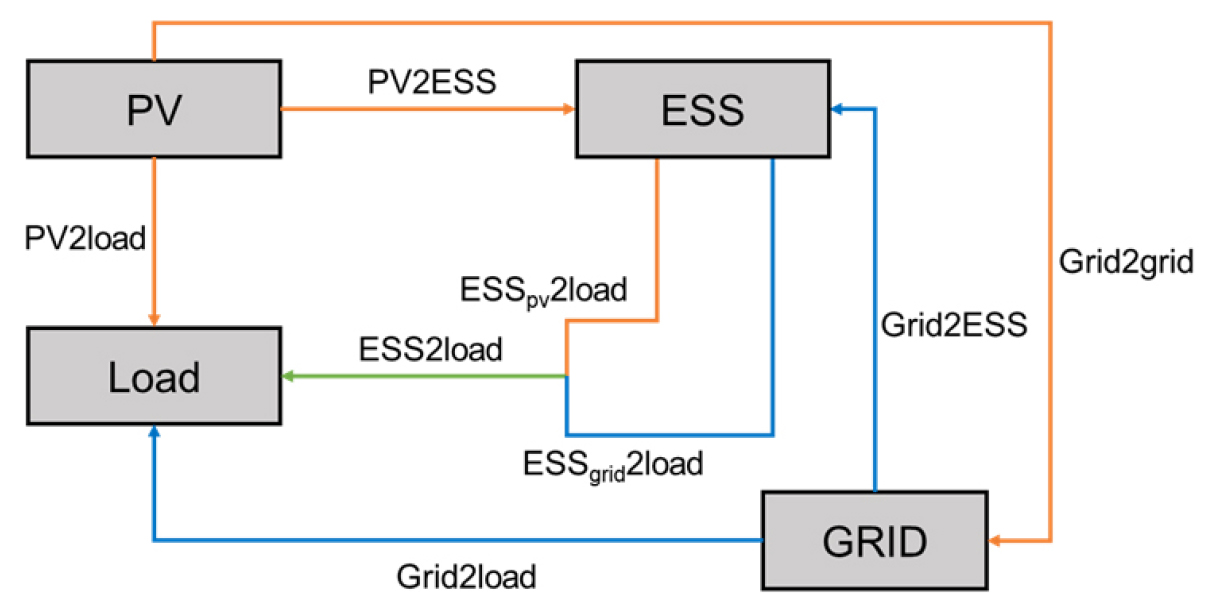
- The impact of the integrated operation of photovoltaic (PV) and energy storage system (ESS) units on the energy SCR and SSR within …
- The impact of the integrated operation of photovoltaic (PV) and energy storage system (ESS) units on the energy SCR and SSR within an industrial park were investigated. The load characteristics of industrial parks, unlike those of general commercial facilities, are highly heterogeneous owing to their diverse process operations, varying load profiles, daytime operation rates, and peak power demands. Consequently, even if industrial parks and general commercial facilities have identical PV installation capacities, the resulting SCR and SSR widely differ depending on the operational characteristics of the site. Therefore, establishing an effective DER operation strategy for RE100 implementation in industrial parks requires an analytical framework that reflects the real-time matching between PV generation and load profiles as well as the capability of the ESS to store and reuse surplus energy. On-site renewable generation was studied as an RE100 compliance measure. and the SCR and SSR were analyzed based on annual operational data from PV and ESS systems using the actual electricity consumption characteristics of an industrial park. The annual SCR and SSR were 85.16% and 27.09%, respectively, under the evaluated conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Energy Self-Consumption Ratio and Self-Sufficiency Ratio in PV-ESS Integrated Systems for Industrial Park RE100
-
Research Article
-
Fluorine-Free Transparent Backsheets for Low-Carbon Footprint Photovoltaic Modules
저탄소 태양광 모듈을 위한 비불소계 투명 백시트
-
Kwon Da Young, Park Yerang, Han Jae-Ik, Park Nochang, Bae Soohyun, Kim Kyung-Soo, Eo Young-Joo, Kang Gi-Hwan, Lee Yonghwan
권다영, 박예랑, 한재익, 박노창, 배수현, 김경수, 어영주, 강기환, 이용환
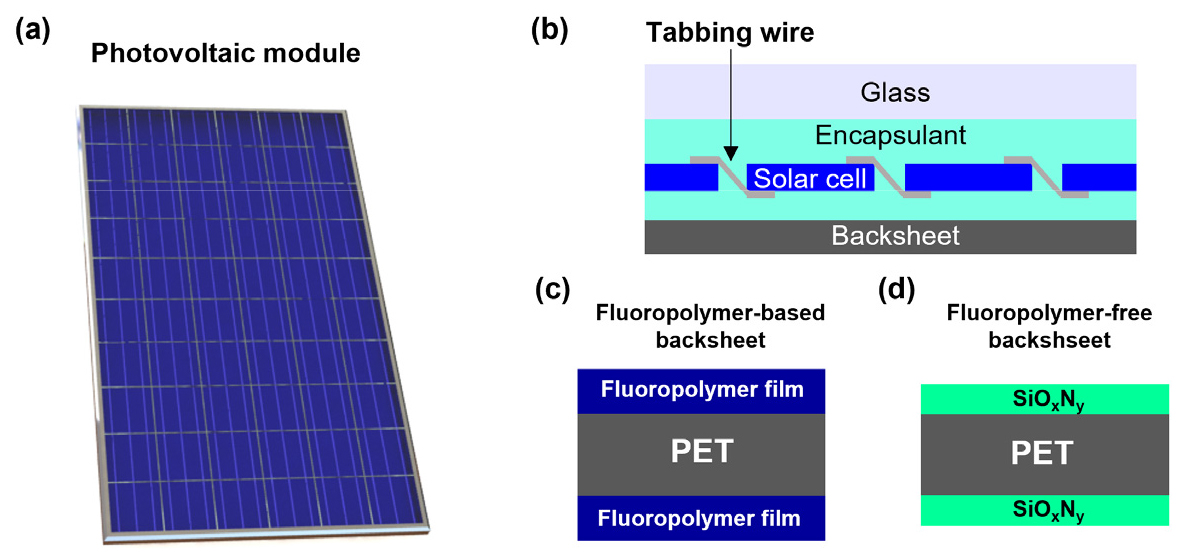
- Fluorine-free transparent photovoltaic backsheets were developed via dip-coating polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films with perhydropolysilazane (PHPS), which were subsequently converted to a SiO …
- Fluorine-free transparent photovoltaic backsheets were developed via dip-coating polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films with perhydropolysilazane (PHPS), which were subsequently converted to a SiOxNy-based inorganic coating layer on the PET surface. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy confirmed the formation of Si–O, Si–N, and Si–OH bonds, effectively converting the PHPS precursor into a robust SiOxNy network. UV–Vis measurements revealed that the optical transmittance of the coated films was high (>88%), ensuring optical suitability for photovoltaic transparent backsheet applications. The water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) measurements demonstrated that the moisture permeability (<2 g/m2·day) was lower than that of the untreated PET films, whereas the adhesion tests confirmed strong interfacial bonding between the SiOxNy-coated PET film and the encapsulant. Furthermore, the films retained high transparency and strong moisture barrier performance after accelerated aging under pressure-cooker test (PCT) conditions and UV irradiation, confirming their high durability and environmental stability. Overall, SiOxNy-coated PET films are a sustainable, transparent, and high-performance alternative to conventional fluorine-based backsheets for low-carbon photovoltaic modules. - COLLAPSE
-
Fluorine-Free Transparent Backsheets for Low-Carbon Footprint Photovoltaic Modules
-
Research Article
-
Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters Affecting Building Energy Consumption Across Climate Zones
기후대별 건물 에너지 주요 파라미터의 민감도 분석
-
Lee Yujin, Lee Yubin, Choi Mijeong, Shin Dae Uk
이유진, 이유빈, 최미정, 신대욱
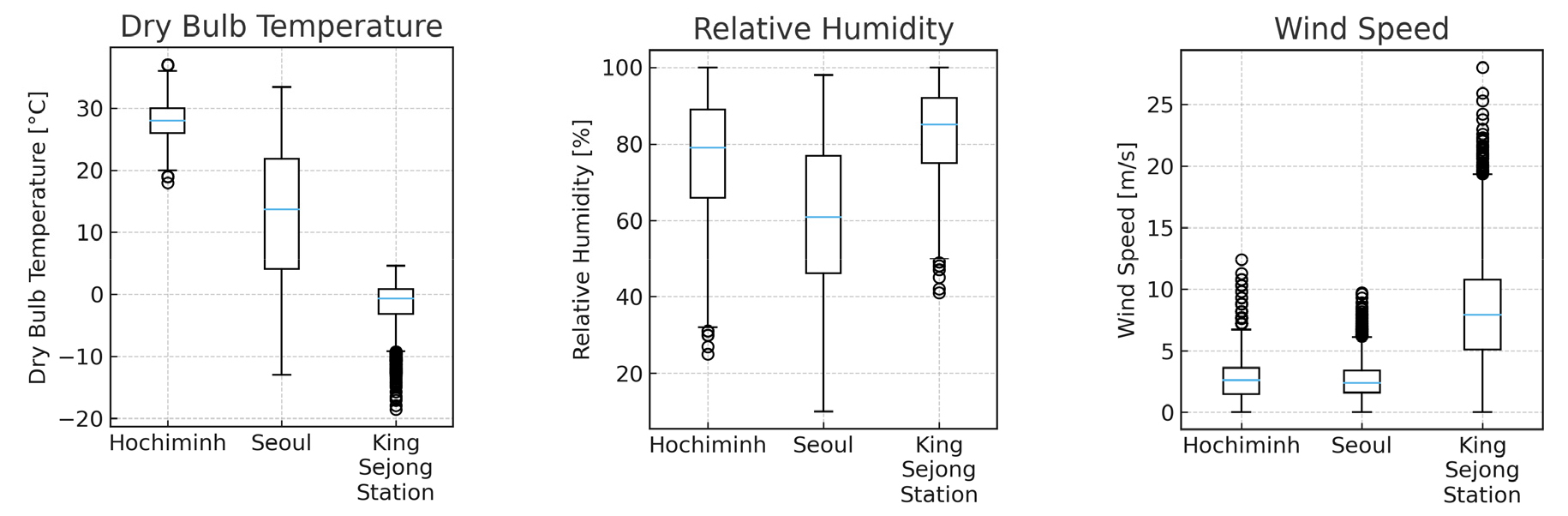
- The parameters that govern building energy consumption must be identified for reducing discrepancies between simulated and measured performance. How climatic conditions affect …
- The parameters that govern building energy consumption must be identified for reducing discrepancies between simulated and measured performance. How climatic conditions affect parameter sensitivity was examined by analyzing specific parameters among three representative Koppen-Geiger climate zones; tropical (Ho Chi Minh City), cold (Seoul), and polar (King Sejong Station). Seven parameters were evaluated using the Morris and Sobol methods. Electric equipment and light densities were consistently the most sensitive in all locations, indicating that the main annual electricity usage was internal heat gains. The coefficient of performance (COP) strongly influenced heating-dominant locations. The sensitivity rankings were consistent between the methods. The close agreement observed between the first-order and total Sobol indices suggested that the effects of the independent parameters accounted for the majority of the variations in the output. - COLLAPSE
-
Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters Affecting Building Energy Consumption Across Climate Zones
-
Research Article
-
Solar Integrated Heat Supply and Smart O&M System for Industrial Process Heat Supply
산업공정용 열공급을 위한 태양열 융합 열공급 및 스마트 O&M 시스템
-
Kim DeokGeun, Kim YoonSu, Yoon YongSoo, Hong HiKi, Song JaeMan
김덕근, 김윤수, 윤용수, 홍희기, 송재만
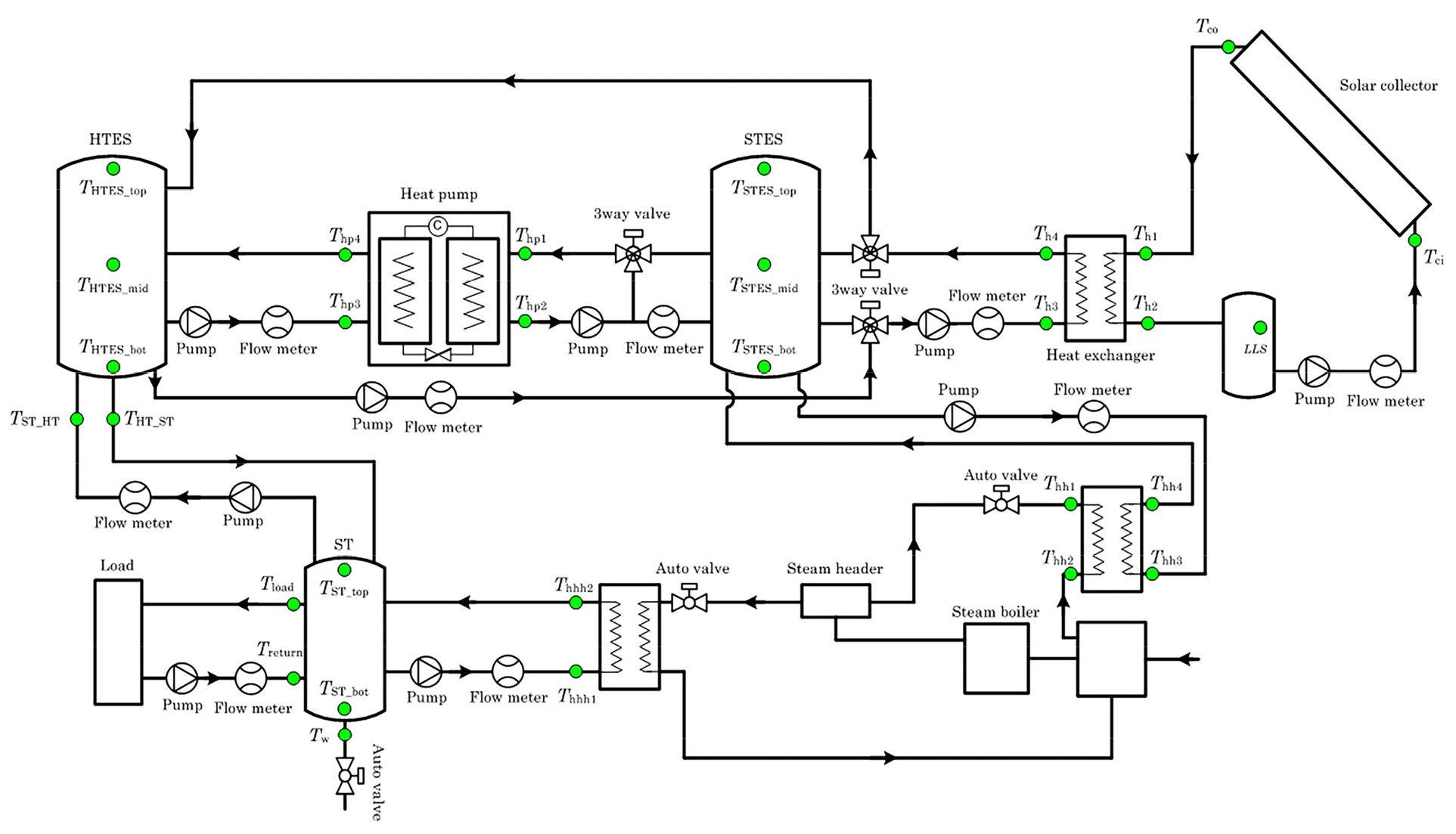
- Solar heat pump hybrid systems must operate stably and their performance must be managed to meet the medium- and low-temperature thermal demands …
- Solar heat pump hybrid systems must operate stably and their performance must be managed to meet the medium- and low-temperature thermal demands of industrial processes using renewable energy. However, solar thermal systems may experience heat source temperatures and failures due to solar radiation fluctuations and equipment aging, necessitating real-time monitoring-based operation and maintenance systems. In this study, a monitoring system for measuring, storing energy, and analyzing solar thermal heat pump hybrid systems in industrial processes in real-time was developed by applying an RS485-based controller and a Python data processing environment. The solar thermal energy storage (STES) was stably maintained within the 40 – 65°C range, and the high-temperature thermal energy storage (HTES) remained within the 70 – 80°C range. The daily performance was analyzed, indicating a system coefficient of performance (SCOP) of 1.9 – 2.1. The renewable fraction (RF) averaged 77%, and the solar fraction (SF) averaged 43%, confirming that 84.3% of the total heat load was covered by renewable energy. The auxiliary boiler heat source covered 15.7% of the total heat load, substantially reducing the dependency on fossil fuels. The established monitoring system is configured to reliably collect key data in 10-second intervals and automatically calculate performance indicators, accurately capturing the operational status. The RS485-Python based architecture facilitates future sensor expansion and field implementation. These results provide foundational data for increasing the operational reliability of the processes of industrial renewable energy heat supply systems and establishing smart operation and maintenance (O&M) frameworks. - COLLAPSE
-
Solar Integrated Heat Supply and Smart O&M System for Industrial Process Heat Supply
-
Research Article
-
Methodology for Establishing a Long-Term Durability Evaluation Process for Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) Modules
BIPV 모듈의 장수명 평가 프로세스 수립을 위한 방법론 연구
-
Jeon Mu-Yi, Ju Chang-Ki, Cho Sung-Dae, Hwang Soo-Hyun, Kim Youn-Hwan
전무이, 주창기, 조성대, 황수현, 김윤환
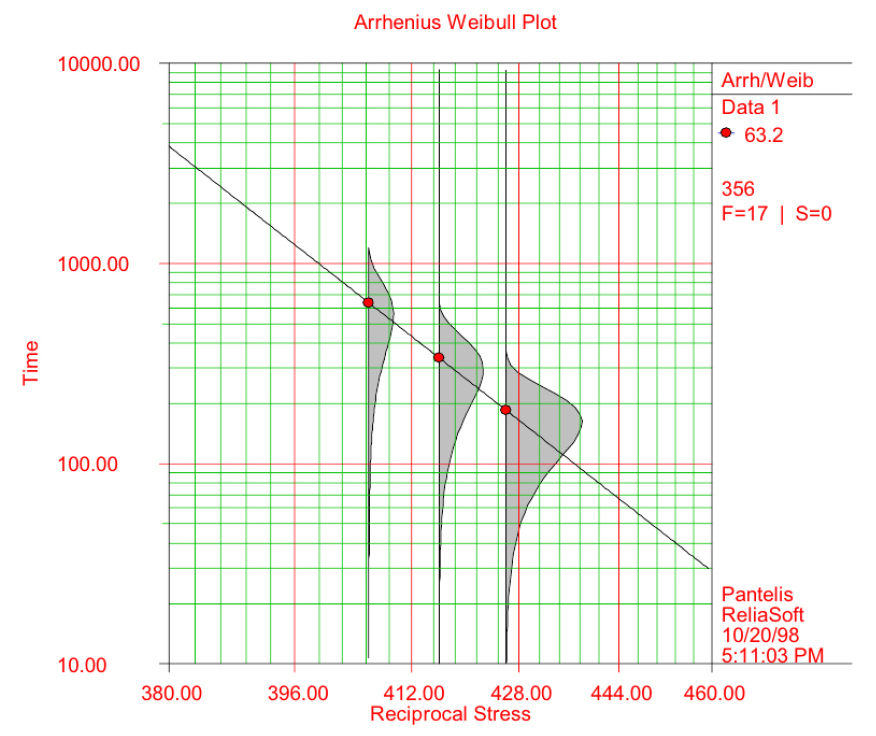
- Building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) modules, which are used as renewable energy sources and building materials, require a higher long-term durability assurance than traditional …
- Building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) modules, which are used as renewable energy sources and building materials, require a higher long-term durability assurance than traditional photovoltaic modules. BIPV modules are structural, fire-resistant, and weatherproof. Moreover, power producers require lifetime guarantees that satisfy the demand for traditional construction materials, often reaching 40–50 years or the full lifetime of the construction. However, recent PV module reliability standards and test manuals, such as IEC 61215, are not fully appropriate for ensuring the long-term environmental stresses experienced by BIPV modules in environmental variations. This study introduces and reviews the certification requirements of major BIPV standards and analyzes the failure states unusual to the integration of building envelopes with PV modules. Based on this analysis, we proposed an accelerated lifetime testing (ALT) methodology that simulates long-term multivariate environmental stress situations within a condensed timeline. The ALT method focuses on major degradation processes, including damp heat, UV exposure, thermal cycling, mechanical load, and other environmental stresses. Specific test procedures were proposed for each critical failure mode. These findings promote design revisions and material blueprints tailored to building applications, accelerate the adoption of rising BIPV technologies, and provide scientific support for future reliability guarantees. This study suggests enhancing trust, adoption, and competitiveness of BIPV products in the global market for sustainable building applications. - COLLAPSE
-
Methodology for Establishing a Long-Term Durability Evaluation Process for Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) Modules
-
Research Article
-
Modeling and Simulation of a Thermal Network Using Power-to-Heat Equipment for Building Clusters
전력-열 변환(P2H) 기기 이용 건물군 열 네트워크의 모델링 및 시뮬레이션
-
Muhammad Farooq, Kwon Si-eun, Lim Byung-Ju, Cho Sung-Hoon, Lee Ga-Ram, Park Chang-Dae
파룩, 권시은, 임병주, 조성훈, 이가람, 박창대
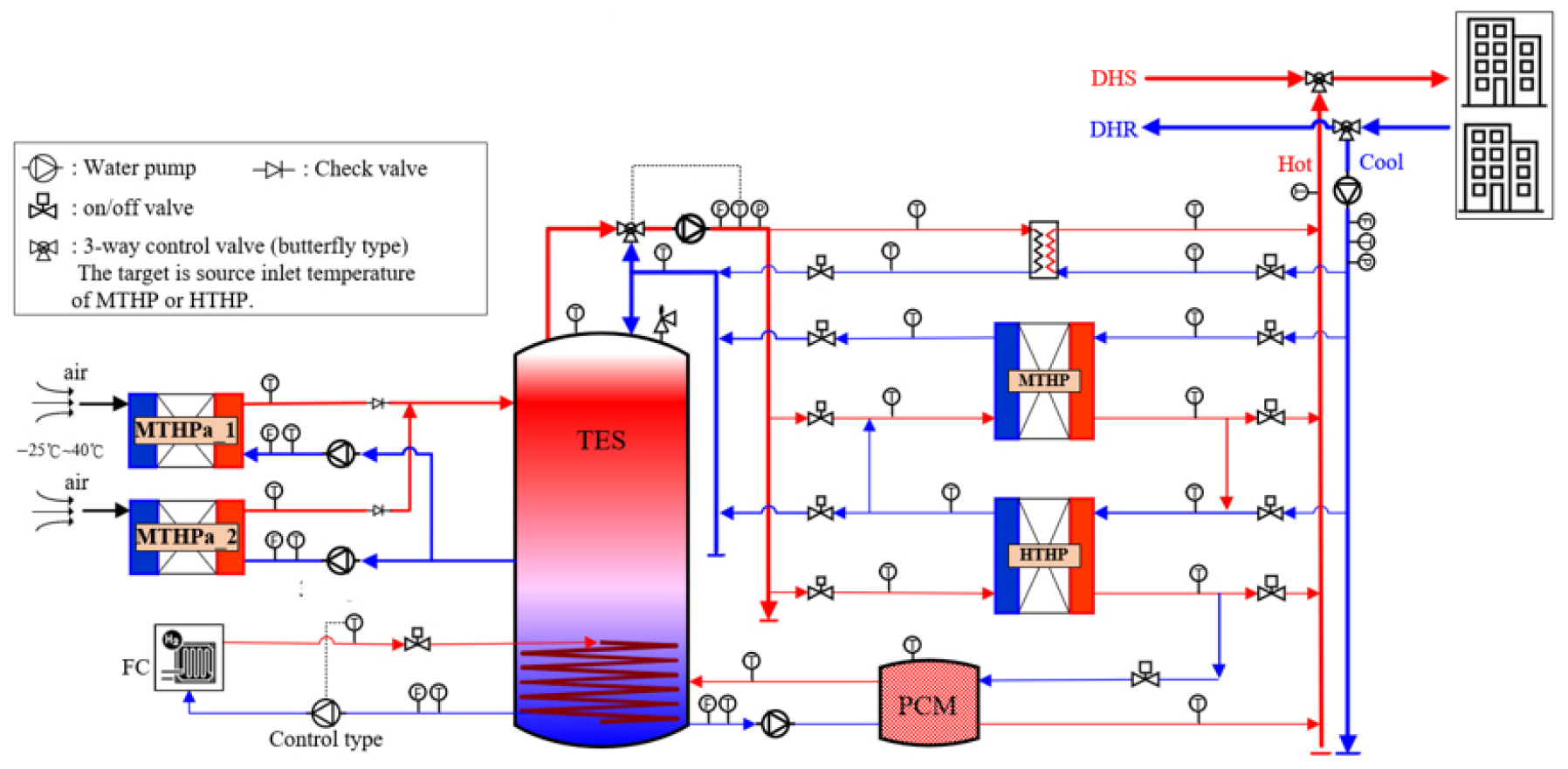
- The rapid expansion of renewable energy systems poses challenges to grid stability and energy balance owing to the intermittent nature of these …
- The rapid expansion of renewable energy systems poses challenges to grid stability and energy balance owing to the intermittent nature of these systems. To address these challenges, integrating reliable heat and electricity storage with power-to-heat technologies has become essential in building energy networks. We focused on developing and demonstrating a thermal demand management system for building clusters that integrates heat pumps, thermal energy storage (TES), and electrical energy storage to absorb variability, reduce peak demand, and enable gridresponsive operation. The system operates under multiple modes, including TES charging and discharging, direct load supply, and parallel or cascade operation, depending on the load conditions, TES state, and demand response signals. To this end, operation modes, control logic, and operational scenarios were established, and a validated TRNSYS simulation model was developed. Ongoing work will involve year-long simulations to align electric and thermal scenarios, optimize operating strategies, and identify the most efficient and flexible demand management approaches. The outcomes are expected to contribute to the development of optimal, grid-responsive, and economically efficient control strategies for electrified building energy systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Modeling and Simulation of a Thermal Network Using Power-to-Heat Equipment for Building Clusters
-
Research Article
-
Evaluation Analysis of Building Energy Efficiency Rating for Apartment Complexes
공동주택 건축물 에너지효율등급 분석평가
-
Kim Ji Hyeon, Choi Hyun Sic, Shin U Cheul
김지현, 최현식, 신우철
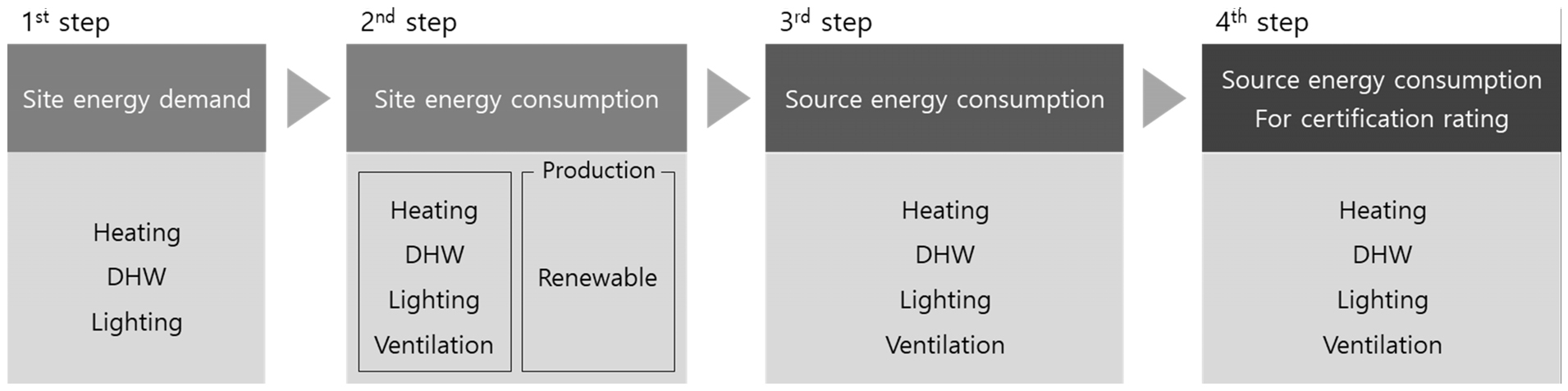
- This study examined the factors contributing to variations in building energy efficiency ratings among apartment complexes constructed under identical insulation standards and …
- This study examined the factors contributing to variations in building energy efficiency ratings among apartment complexes constructed under identical insulation standards and climatic conditions. A total of 88 apartment complexes located in Seoul and Gyeonggi Provinces were analyzed using preliminary certification data from the ECO2 program, including site energy demand, site energy consumption, and source energy consumption. To evaluate the statistical significance of differences between certification grades, Welch’s analysis of variance (Welch’s ANOVA) was applied, while considering potential violations of the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variance. Results indicated that while site energy demand was generally consistent across certification grades, site heating energy consumption exhibited statistically significant differences—particularly in complexes employing individual heating systems, which demonstrated lower system efficiency. In addition, differences in the installed capacity of solar photovoltaic systems were found to partially explain variations in the overall energy efficiency ratings. These findings suggest that the heating system efficiency and integration of renewable energy technologies are key determinants of building energy performance ratings and provide a valuable basis for future energy policy and planning. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation Analysis of Building Energy Efficiency Rating for Apartment Complexes
-
Research Article

-
Evaluation of Electrical and Thermal Prediction Accuracy for a Colored BIPV Facade Using the System Advisor Model (SAM)
컬러 BIPV 외벽 시스템의 전기·온도 성능 실측 및 SAM 기반 예측 정확도 평가
-
Kim Jinhee, Kim Sangmyung, Kim Hayoung, Jeong Subin, Kim Juntae
김진희, 김상명, 김하영, 정수빈, 김준태
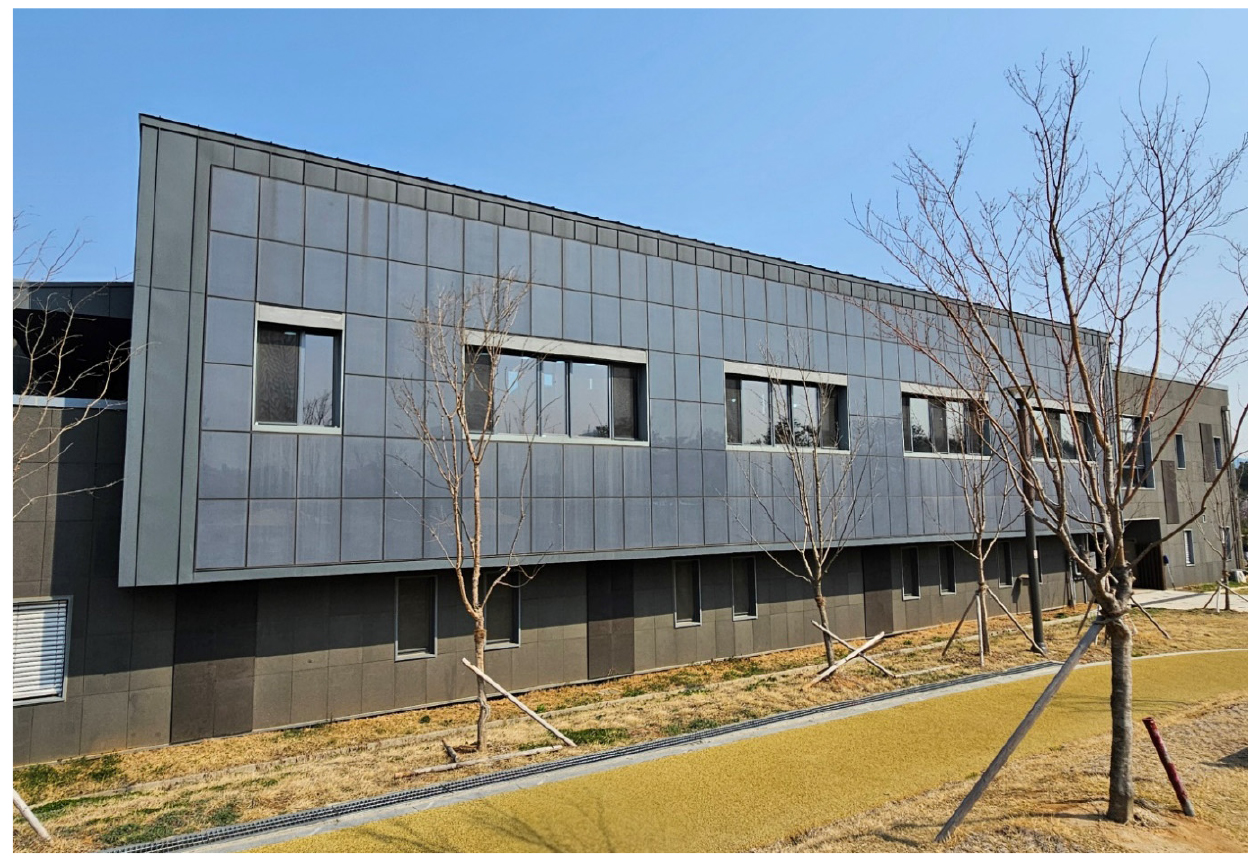
- As the deployment of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) continues to expand, ensuring the reliability of simulation tools used to predict the performance of …
- As the deployment of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) continues to expand, ensuring the reliability of simulation tools used to predict the performance of modules with diverse optical and material characteristics has become increasingly important. In this study, we evaluated the accuracy of the System Advisor Model (SAM) in reproducing the actual operating performance of colored façade-integrated BIPV modules manufactured using ceramic ink dot-pattern technology. A 3.31 kWp façade BIPV subsystem connected to a 3.5 kW inverter at the Asan Youth Library in South Korea was monitored from October 2023 to March 2024. Frequent inverter clipping occurred during periods of high irradiance because the site’s operational constraints prohibited exporting power to the grid. Thus, the subsystem was especially suitable for a detailed performance evaluation. The monitored results showed a total power generation of 1,153 kWh (DC) and 1,107 kWh (AC), with an average module back-surface temperature of 15.3 °C. SAM predicted the annual energy yield with relatively low bias (with a normalized mean bias error (nMBE) = +3.4% for DC and –2.7% for AC) and exhibited a reasonable long-term agreement with the measurements. However, short-term prediction accuracy was limited, as reflected by the high normalized root mean square error (nRMSE) values of 26.4% (DC) and 32.4% (AC). These deviations indicate that the unique optical and thermal characteristics of ceramic dot-pattern colored modules, such as variations in spectral transmittance, non-uniform optical losses, and constrained façade ventilation, are not fully captured by SAM’s standard PV performance and temperature models. Thus, this study provides one of the first real-building validations of the SAM for colored façade-integrated BIPV systems in South Korea. These findings highlight the need for improved optical and thermal modeling, as well as module-specific correction factors, to enhance the accuracy of simulations for practical applications of colored BIPV systems. The results also serve as a valuable reference for the future design, modeling, and performance prediction of colored BIPV systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of Electrical and Thermal Prediction Accuracy for a Colored BIPV Facade Using the System Advisor Model (SAM)
-
Research Article

-
Comparative Study on Wake Characteristics of Dual-Rotor Wind Turbines under Varying Thrust Coefficient and Turbulence Intensity
추력계수와 난류강도 변화에 따른 듀얼로터 풍력터빈 후류 특성 비교 연구
-
Kim Hyungyu, Hur Chihoon, Ko Dongkyu
김현규, 허치훈, 고동규
- In this study, we investigated the wake characteristics of dual-rotor wind turbines through simulations of the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and compared …
- In this study, we investigated the wake characteristics of dual-rotor wind turbines through simulations of the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and compared the results with those of single-rotor turbines and conventional engineering wake models. Using the NREL WindSE software package based on the FEniCS project with the actuator line method, simulations were conducted for two inflow wind speeds (8 and 12 m/s) and two turbulence intensity levels (10.22% (low TI) and 14.6% (high TI)) to analyze the impact of variations in the thrust coefficient on wake behavior. The results indicated that dual-rotor systems exhibited greater velocity deficits than single-rotor turbines, with an average increase of 14.5% (low TI) and 13.8% (high TI) in the below-rated region, which was reduced to 5.8% in the above-rated region due to decreased thrust coefficients. Notably, vortex interactions between rotors caused some deflection of the centerline of the wake that was not observed in single-rotor systems. This deflection increased the contact with the freestream flow, which accelerated wake recovery rates by up to 23.1% compared with single rotors. Conventional engineering wake models (Bastankhah and Jensen Gaussian) successfully predicted overall Gaussian velocity deficit patterns but failed to capture the deflection of the centerline of the wake caused by vortex interactions. The prediction errors decreased with lower turbulence intensity and below-rated thrust coefficients, with errors increasing by a factor of approximately 1.6 in conditions with a high thrust coefficient. These findings provide fundamental quantitative data on the wake characteristics of dual-rotor wind turbines. They can also serve as a technical foundation for the optimization of the layout of wind farms and the development of specialized wake models for dual-rotor systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative Study on Wake Characteristics of Dual-Rotor Wind Turbines under Varying Thrust Coefficient and Turbulence Intensity
-
Research Article
-
Evaluating the Contribution of Metropolitan Governments’ Renewable Energy Deployment Plans to Building Electrification: Implications for Achieving the 2035 NDC Target
광역지자체 건물부문 신재생 에너지 보급 계획의 전기화 기여도 평가: 2035 NDC 목표 달성 가능성을 중심으로
-
Shin Hyery
신혜리
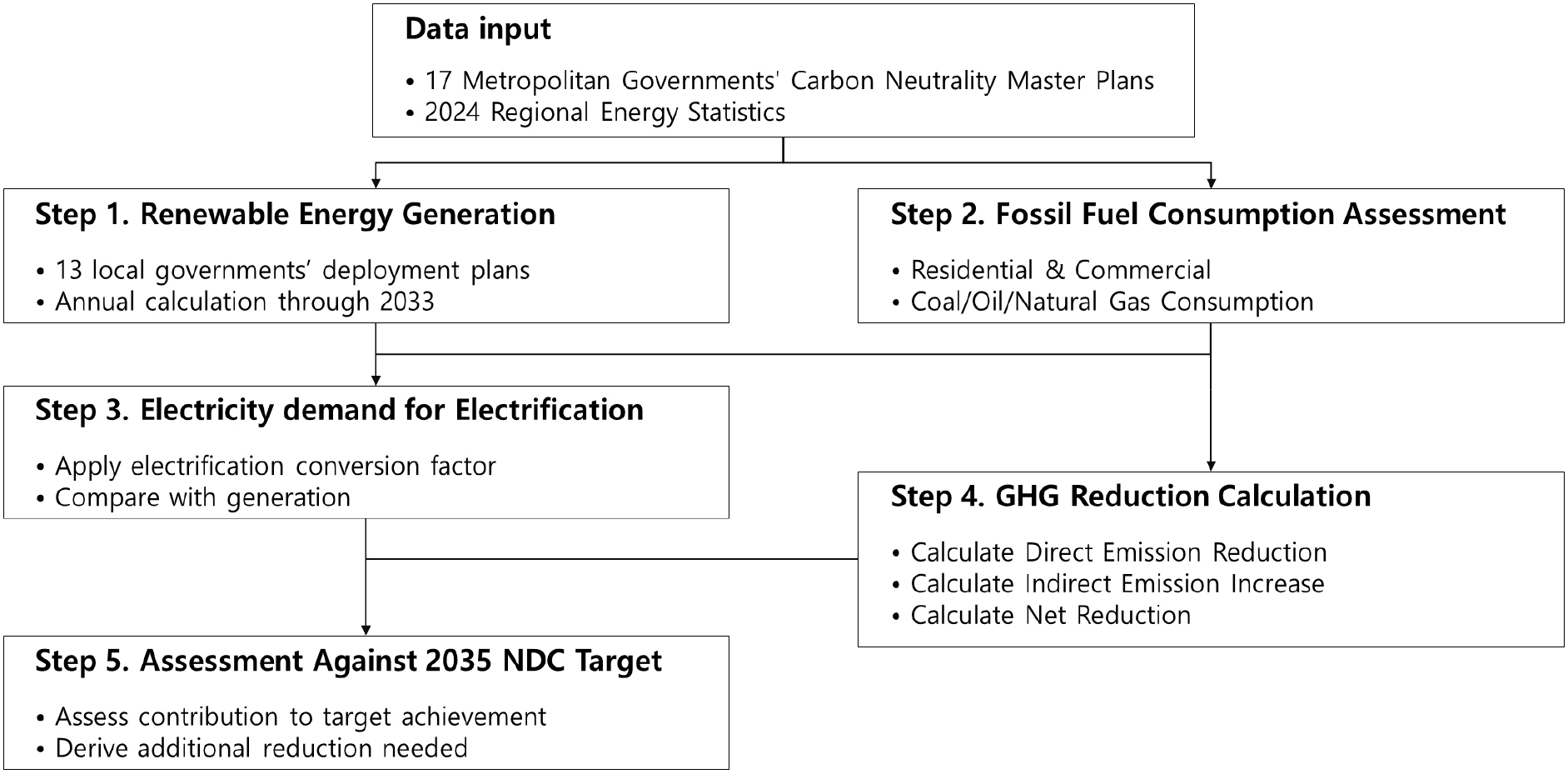
- In this study, we quantitatively evaluated the extent to which building electrification derived from the renewable energy deployment plans of 13 metropolitan …
- In this study, we quantitatively evaluated the extent to which building electrification derived from the renewable energy deployment plans of 13 metropolitan governments can contribute to achieving South Korea’s 2035 Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) target for the building sector. To that end, we analyzed the renewable energy deployment plans presented in local governments’ carbon neutrality and green growth master plans to estimate electricity generation through 2033. We also calculated the electricity demand and greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction potential associated with replacing fossil fuel-based heating and hot water systems in residential and commercial buildings with electric heat pumps. The results show that renewable energy generation in 2033 (236,330 GWh) is expected to exceed electrification demand by a factor of 3.6, which corresponds to a national average coverage rate of 368.7%. However, pronounced regional disparities were observed, with coverage ranging from 1,830.7% in Chungnam to 18.6% in Jeju. The net GHG reduction of 11.2 MtCO2eq represents approximately 38% – 40% of the 2035 NDC target for the building sector. These findings indicate that the existing renewable energy deployment plans can make a substantial contribution toward achieving the NDC target. However, meeting the required GHG reduction levels will necessitate a combination of diverse policy measures and integrated planning across the building and power sectors. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluating the Contribution of Metropolitan Governments’ Renewable Energy Deployment Plans to Building Electrification: Implications for Achieving the 2035 NDC Target
-
Research Article
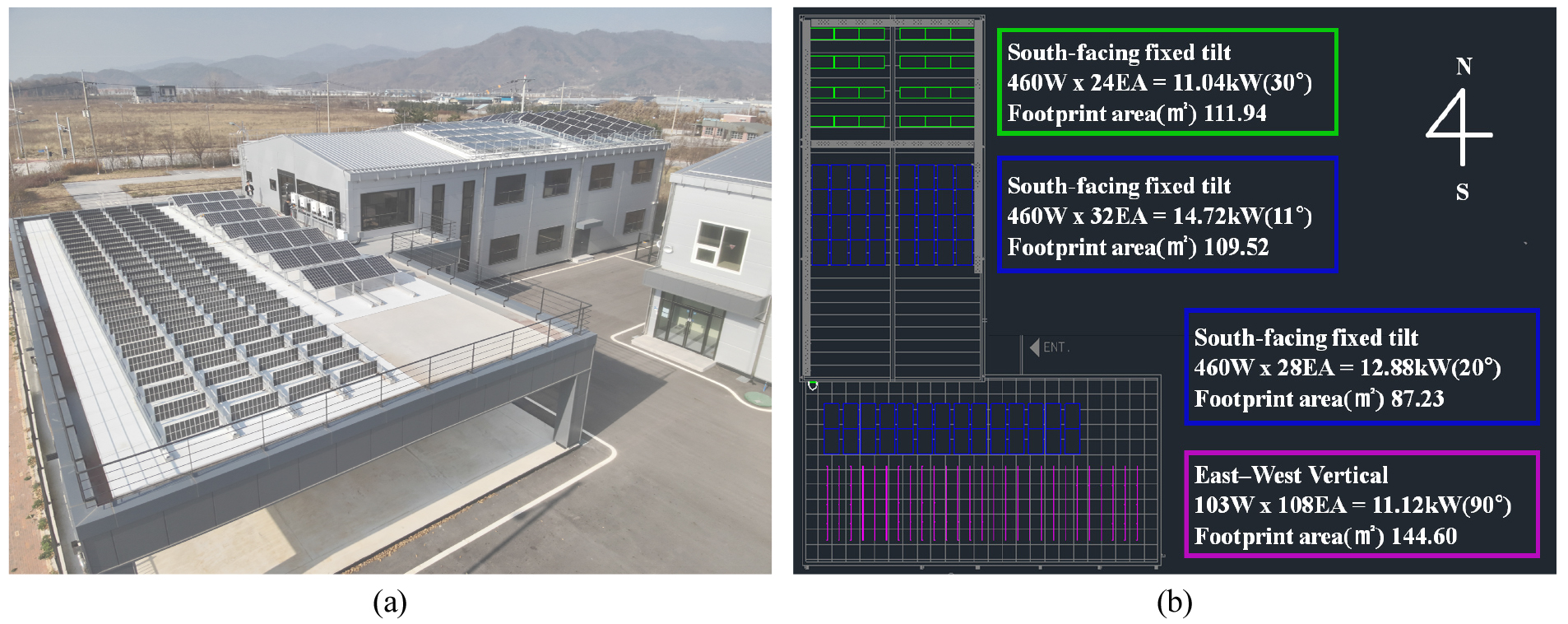
-
Empirical Analysis of Power Generation and Peak-Dispersion Characteristics of East-West Oriented PV Systems
동서형 태양광의 경사각 및 설치형태에 따른 발전특성과 피크 분산효과 실증 분석
-
Jeong Seung-Hwan, Kim Yu-Ri, Yoo Jeong-Hee, Sim Hoon
정승환, 김유리, 유정희, 심훈
- The rapid expansion of photovoltaic (PV) deployment in Korea has intensified the midday generation peak associated with conventional south-facing fixed-tilt systems, contributing …
- The rapid expansion of photovoltaic (PV) deployment in Korea has intensified the midday generation peak associated with conventional south-facing fixed-tilt systems, contributing to an increase in curtailment events and greater stress on the power grid. East-West (EW) PV configurations have drawn attention as a potential mitigation strategy; however, empirical performance evaluations considering different tilt angles and installation types remain limited. This study analyzed the power generation characteristics and peak-dispersion performance of EW-oriented PV systems installed on an industrial gable roof and a flat-slab rooftop. An eight-month field experiment was conducted from April to November 2025 using a south-facing fixed-tilt system as a reference. Three EW configurations were tested: an 11° dual-slope system on the gable roof and 20° dual-slope and 90° vertical systems on the flat slab. The analysis focused on the monthly energy yield, capacity factor, peak-dispersion behavior, and ground coverage ratio, with particular emphasis on whether EW systems can alleviate the grid burden during hours when curtailment is typically enforced. Results showed that all EW configurations exhibited a noticeable reduction in the midday generation peak compared with that of the south-facing reference. This peak-flattening effect effectively suppressed excessive output during curtailment-prone hours, demonstrating the structural advantages of EW-oriented PV systems in reducing grid stress and lowering the likelihood of curtailment. - COLLAPSE
-
Empirical Analysis of Power Generation and Peak-Dispersion Characteristics of East-West Oriented PV Systems
-
Corrigendum
-
CORRIGENDUM to Analysis of Power Generation and Indoor Illuminance of Photovoltaic Blinds
태양광 블라인드의 발전량 및 실내 조도 분석
-
Hong Chai-Min, Heo Jae-Baek, Park Sang-Hoon
홍채민, 허재백, 박상훈
-
CORRIGENDUM to Analysis of Power Generation and Indoor Illuminance of Photovoltaic Blinds
-
Corrigendum
-
CORRIGENDUM to Performance Evaluation of a Natural Solar Lighting and LED Hybrid Louver Window System for Energy Saving in Indoor Vertical Farm
식물공장의 조명 전력에너지 절감을 위한 태양광 LED 하이브리드 루버 외피기술 성능 평가
-
An Youngsub, Kieu Ngoc Minh, Joo Hong-Jin, Lee Kyoung-Ho, Lee Hyun-Hee, Shin Seoyong, Kang Sae-Byul
안영섭, Kieu Ngoc Minh, 주홍진, 이경호, 이현희, 신서용, 강새별
-
CORRIGENDUM to Performance Evaluation of a Natural Solar Lighting and LED Hybrid Louver Window System for Energy Saving in Indoor Vertical Farm
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society











