-
Research Article
-
Understanding Electric Properties Thickness of SnO2 with Atomic Layer Deposition
원자층 증착법을 활용한 SnO2의 두께에 따른 전자 이동도 분석
-
Siwon Yun, Kihyun Kim, Minkyu Kim, Minji Jung, Wonjong Lee, Hyeji Han, Hyosik Chang, Jongchul Lim
윤시원, 김기현, 김민규, 정민지, 이원종, 한혜지, 장효식, 임종철
- Wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells enable high open-circuit voltages, which are crucial for tandem solar cells, but suffer from increased recombination and stability …
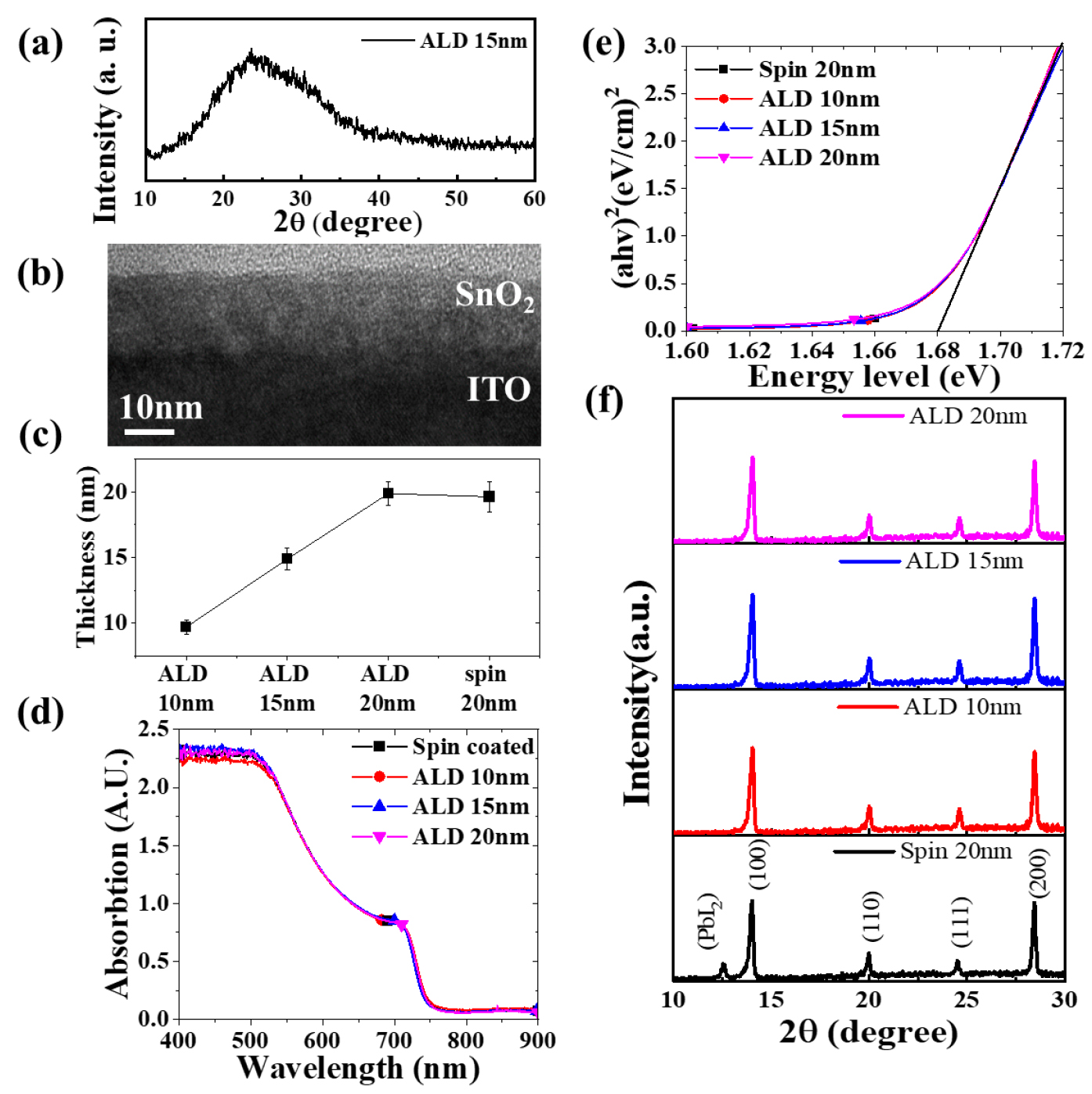
- Wide-bandgap perovskite solar cells enable high open-circuit voltages, which are crucial for tandem solar cells, but suffer from increased recombination and stability issues owing to bandgap-induced structural and interfacial defects. We precisely tuned the SnO₂ thickness via atomic layer deposition and used time-resolved photoluminescence and pulsed-voltage space-charge-limited current analyses to investigate charge transport and recombination. These results reveal the critical influence of the electron transport layer (ETL) thickness on the electric field distribution and interfacial recombination, providing design guidelines for high-efficiency, stable tandem top cells. This study advances the development of next-generation photovoltaic devices. - COLLAPSE
-
Understanding Electric Properties Thickness of SnO2 with Atomic Layer Deposition
-
Research Article
-
Optimal Operation of EHP for Reducing Energy Consumption in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems
순환여과식 양식장의 에너지 사용량 저감을 위한 EHP의 최적 운영
-
Jangho Hong, Naekyung Kim, Jabin Goo, Yongmok Kim, Sehjoon Dokko, Seng- Kyoun Jo, Younghoon Kwak, Sunhye Mun
홍장호, 김내경, 구자빈, 김용목, 독고세준, 조성균, 곽영훈, 문선혜
- Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) have high energy consumption because of the operation of various types of equipment. In particular, in facilities that …
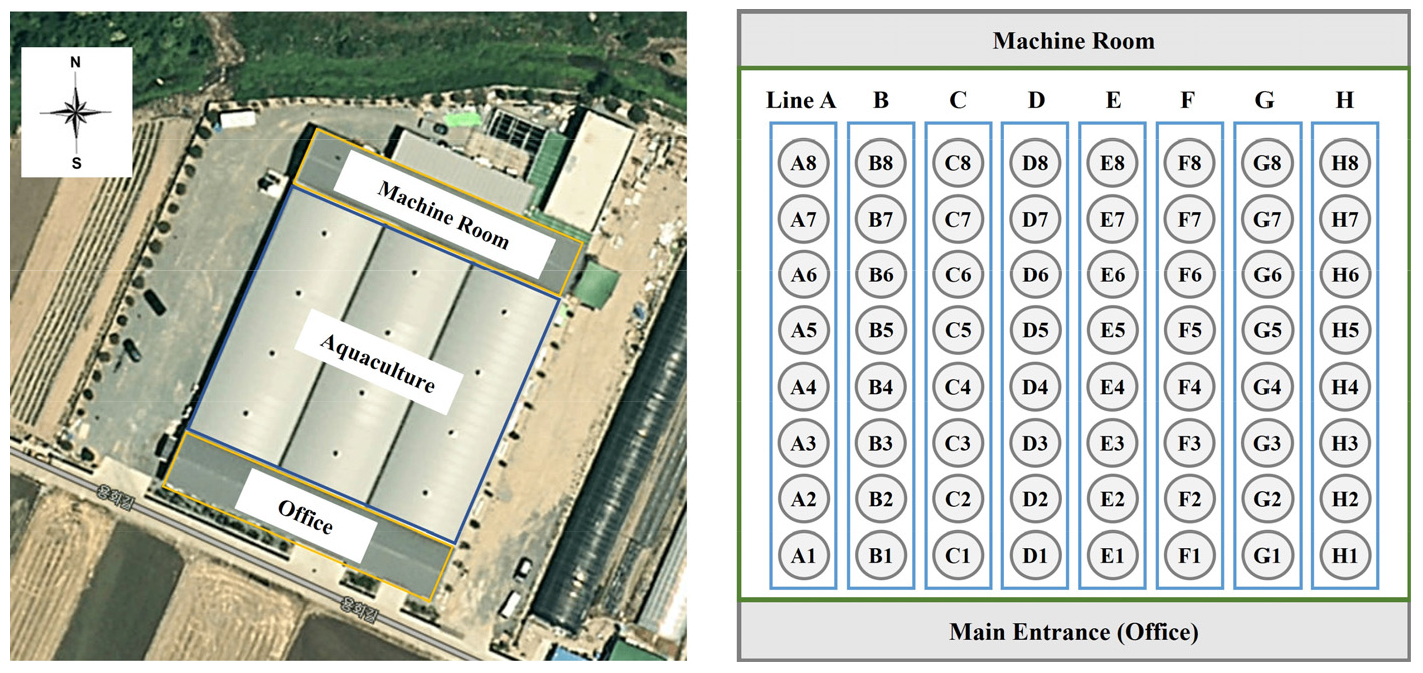
- Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) have high energy consumption because of the operation of various types of equipment. In particular, in facilities that cultivate warm-water species, boiler loads increase significantly during winter to maintain appropriate water temperatures under low outdoor air conditions. This load can be partially mitigated by heating indoor air through HVAC operations; however, reducing relative humidity increases water evaporation from tanks, and the inflow of replenished groundwater subsequently lowers water temperature, resulting in additional heating demand. Therefore, the energy consumption of aquaculture facilities must be comprehensively analyzed, accounting for both water temperature and indoor air conditions. This study investigates the application and operation of an electric heat pump (EHP) as an energy-saving strategy during winter in a recirculating aquaculture facility. For validation, measurements and verification were conducted by collecting field data on indoor air temperature and humidity, water temperature, dissolved oxygen, and electrical consumption. The calibrated model achieved an MBE accuracy level of –0.37% and a Cv(RMSE) of 11.9%. Based on this validated baseline model, an EHP system was integrated, and optimal operation strategies were derived based on indoor air temperature. This study demonstrated the potential to reduce energy consumption through HVAC applications in indoor aquaculture facilities, which are classified as energy-intensive buildings. - COLLAPSE
-
Optimal Operation of EHP for Reducing Energy Consumption in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop according to the Installation Location and Arrangement of Vortex Generators in a Finned Air Channel of a Solar Air Collector
핀 채널이 있는 태양열 공기 집열기 내 와류 생성기 부착 위치 및 배치에 따른 열전달 및 압력강하 성능 분석
-
Taehwan Choi, Hyeonseok Jeong, Geonyong An, Kwangam Moon, Hwiung Choi
최태환, 정현석, 안건용, 문광암, 최휘웅
- The solar-air collector is a renewable energy system that recovers solar thermal energy using air. Unlike liquid-type solar collectors, they can obtain …
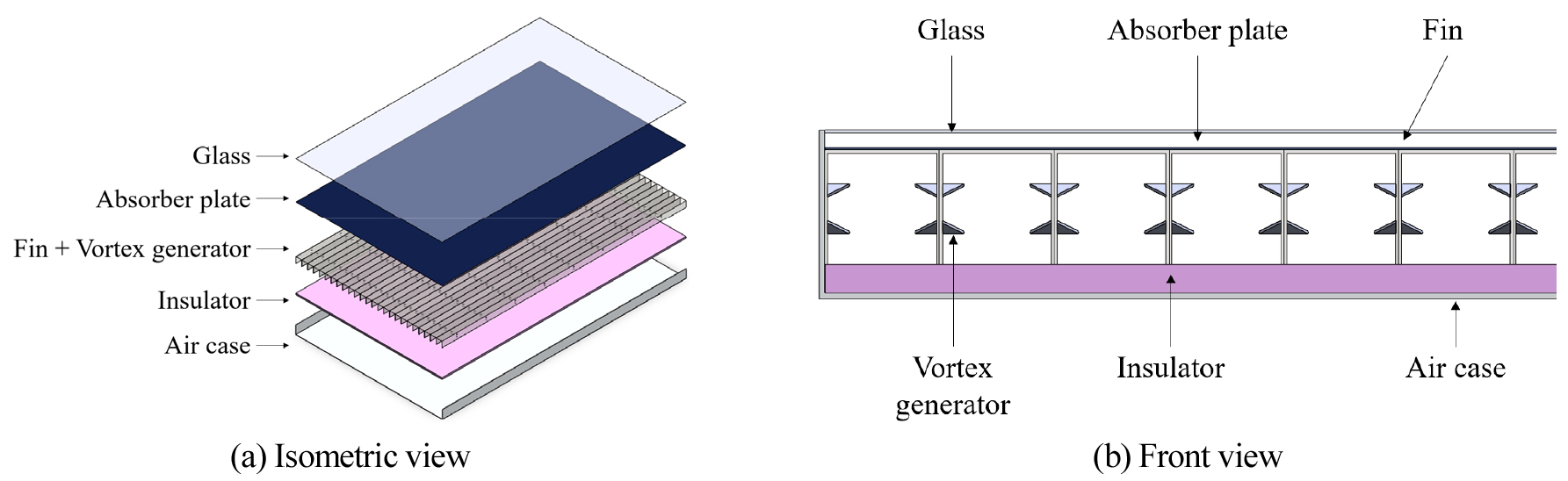
- The solar-air collector is a renewable energy system that recovers solar thermal energy using air. Unlike liquid-type solar collectors, they can obtain thermal energy without requiring large-scale equipment. However, its thermal efficiency must be improved due to the low thermal conductivity of the air. In this study, the heat transfer and pressure drop in a solar–air collector with a finned air channel were evaluated when vortex generators were attached to the fin surfaces. Six configurations were analyzed based on installation location and vortex generator arrangement at Reynolds numbers ranging from 3,000 to 15,000. The results confirmed that the vortex generator improved the heat transfer performance by up to 2.36 times. However, the friction factor increased by up to 4.11 times. Hence, the thermal-hydraulic performance was assessed by considering both improvements in heat transfer and increases in pressure drop. The best performance was achieved when the vortex generators were attached only to the vertical surface of the fins, in an arrangement that expanded the area along the airflow direction. These results are expected to provide valuable information for the further development of air heaters. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop according to the Installation Location and Arrangement of Vortex Generators in a Finned Air Channel of a Solar Air Collector
-
Research Article
-
The Examination of Appropriate Learning Periods to Improve the Prediction Accuracy of Solar Power Generation with a LSTM Model
LSTM 모델을 활용한 태양광 발전량 예측 모델의 예측 정확성 확보를 위한 적정 학습 기간에 관한 연구
-
Yong-Jun Lee, Dong-Su Kim, Eun-Joo Oh, Eui-Hwan Ryu
이용준, 김동수, 오은주, 류의환
- The purpose of this study is to develop a PV power generation machine learning model using the LSTM model, verify its accuracy, …
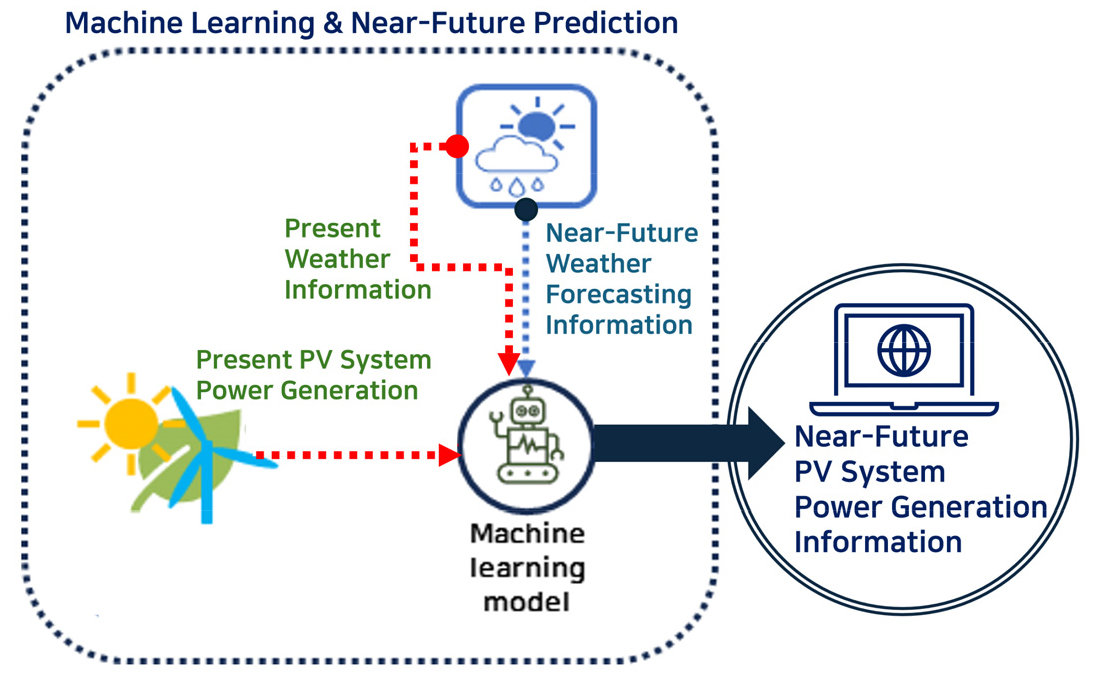
- The purpose of this study is to develop a PV power generation machine learning model using the LSTM model, verify its accuracy, and derive an appropriate learning period to ensure the appropriateness of the solar power generation prediction model. A comparison of short-term power generation data predicted by the machine learning model with data measured at the corresponding forecast time showed R2 = 0.9499, indicating sufficient accuracy. Finally, the minimum learning period to secure a certain level of prediction through a review of the prediction result was reviewed using the power generation data already secured and the weather information at the same point during the period; 30 days were calculated as an appropriate learning period to ensure the accuracy of the solar power generation prediction model. - COLLAPSE
-
The Examination of Appropriate Learning Periods to Improve the Prediction Accuracy of Solar Power Generation with a LSTM Model
-
Research Article
-
A Feasibility Study on the Insulation Reinforcement Effect of the North-Facing Apartment Wall
아파트 북측 벽면의 단열 보강 효과에 대한 기초적 연구
-
Byeonghyeon Ryu, Hyunjae Chang
류병현, 장현재
- Korean apartment buildings are traditionally designed with a strong preference for south-facing orientations and balcony extensions are common. The south-facing façades of …
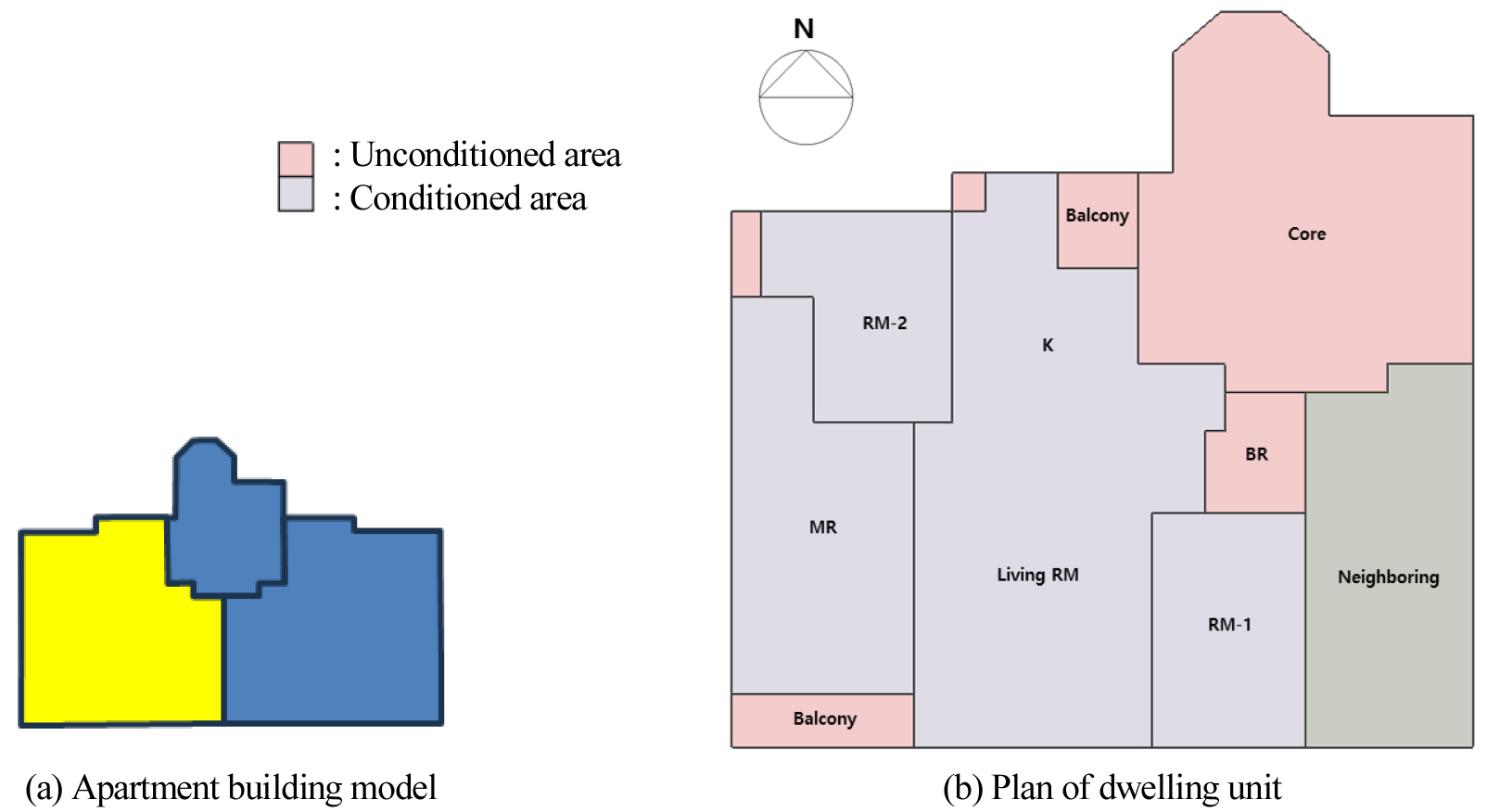
- Korean apartment buildings are traditionally designed with a strong preference for south-facing orientations and balcony extensions are common. The south-facing façades of the dwelling units benefit from solar heat gains during winter owing to the low solar altitude at noon, resulting in relatively low heating loads. In contrast, north-facing façades do not receive direct solar radiation, which inevitably leads to greater heat losses compared with other orientations. Therefore, examining the thermal characteristics of north-facing rooms and quantitatively identifying the effects of the insulation reinforcement of north-facing walls are important for establishing energy-saving strategies for new construction and renovation projects. Accordingly, this study focused on a typical flat-type apartment unit, and the thermal environment and heat transfer during the heating period in rooms facing north were extensively investigated. Additionally, the heating energy-saving effects resulting from the insulation reinforcement of the north-facing walls were evaluated. Consequently, the north-facing room was scarcely influenced by direct solar radiation, and its average indoor temperature in winter under non-heating conditions was approximately 5℃ lower than that of the south-facing room. Although the south-facing room experienced almost no heating load, even during winter, the north-facing room exhibited heating loads of approximately 3–6 kWh/m2 in January–February and December. Insulation reinforcement of north-facing walls reduced the heating load by approximately 7.2–7.9% for the entire dwelling unit, whereas a reduction of 15.8–17.2% was observed when the analysis was limited to a north-facing room. Based on these results, the insulation reinforcement of north-facing walls is expected to be highly effective in reducing the heating energy consumption. - COLLAPSE
-
A Feasibility Study on the Insulation Reinforcement Effect of the North-Facing Apartment Wall
-
Research Article
-
Deep Learning Prediction Model of Surface Solar Radiation and Photovoltaic Power Using Stepwise Overlapped Grouping of Extraterrestrial Radiation
대기권 밖 일사량의 구간별 중복 그룹핑 기법을 적용한 딥러닝 기반 지표면 일사량 및 태양광 발전량 예측 모델
-
Hwangkyu Choi
최황규
- As the proportion of renewable energy sources has increased, the demand for accurate photovoltaic (PV) power forecasting to mitigate its inherent intermittency …
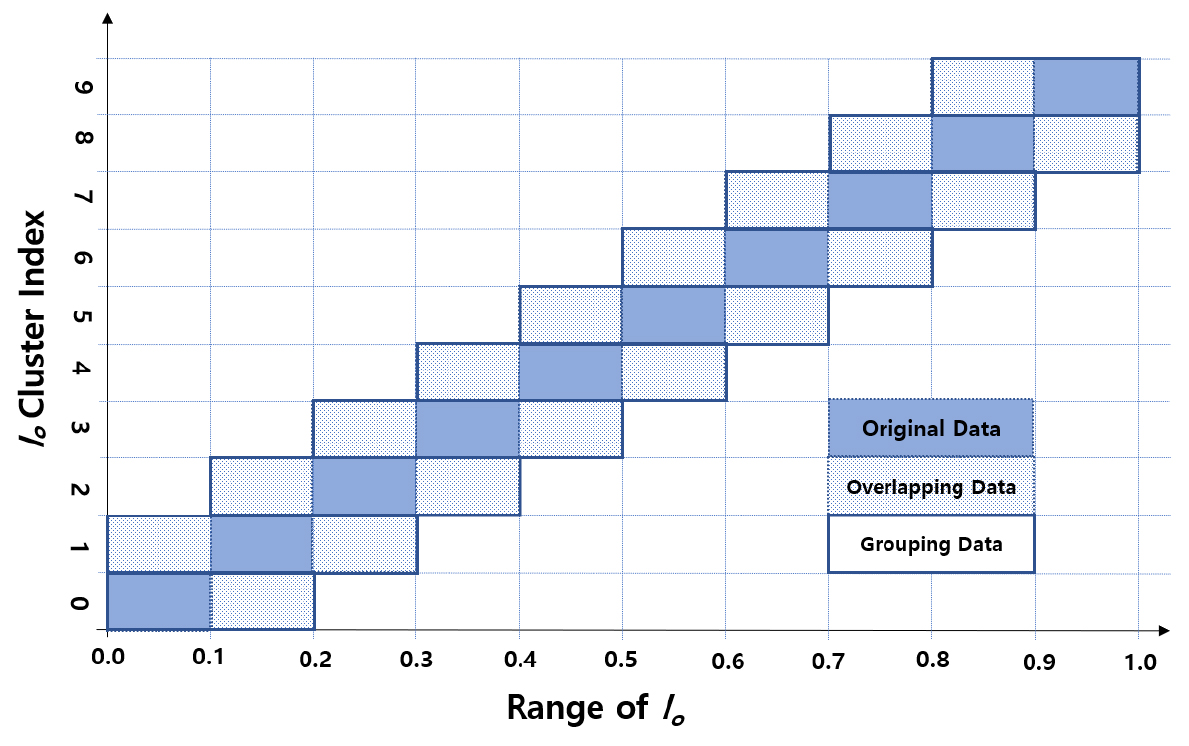
- As the proportion of renewable energy sources has increased, the demand for accurate photovoltaic (PV) power forecasting to mitigate its inherent intermittency has intensified. Although solar radiation is the most critical factor influencing the PV output, the lack of direct irradiance forecasts in standard meteorological systems causes significant prediction uncertainties. This study proposes a two-stage deep learning forecasting model that incorporates extraterrestrial radiation (ESR), a theoretically calculable parameter, using stepwise overlapped grouping. The proposed method categorizes data into intervals based on the ESR intensity, while overlapping the data between adjacent groups. This approach ensures temporal continuity and enhances the adaptability of the model to abrupt weather changes at interval boundaries. Investigations using meteorological and PV power data from Jeju Island demonstrate that the proposed model improves the mean absolute error for solar radiation forecasting by approximately 12.4% when compared to conventional time-based grouping models. Furthermore, the model exhibits high precision in tracking the patterns of actual PV power generation. - COLLAPSE
-
Deep Learning Prediction Model of Surface Solar Radiation and Photovoltaic Power Using Stepwise Overlapped Grouping of Extraterrestrial Radiation
-
Research Article

-
A Study on Rapid Capacity Diagnosis of Used Batteries Using Partial Discharge Data and Polynomial Modeling
부분 충·방전 데이터와 다항식을 활용한 사용후 배터리의 용량 신속 진단 기법에 관한 연구
-
Doheon Lee, Eel-Hwan Kim
이도헌, 김일환
- The demand for second-life utilization of used batteries (UBs) is rapidly increasing with the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and emphasis on …
- The demand for second-life utilization of used batteries (UBs) is rapidly increasing with the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and emphasis on circular economy policies. As of 2025, >3,500 UBs have accumulated domestically, with projections reaching several hundred thousand units by 2030, highlighting the requirement for efficient and scalable performance evaluation techniques for assessing the residual value of UBs. Conventional capacity diagnosis methods such as full-cycle testing in certification systems like Korea Certification require >180 min per unit, imposing significant time and resource burdens. To address this challenge, this study investigated a rapid diagnostic methodology that estimates capacity using partial discharge data and open-circuit voltage measurements. A high-order polynomial regression using the least-squares method was applied and validated through experiments on 20 second-life battery modules. The proposed model achieved a capacity estimation error within ±2% compared with reference measurements, demonstrating reliable accuracy without requiring full charge–discharge cycles. This method enabled diagnosis within approximately 20 min under C/3 discharge conditions. This approach enhances the practicality of large-scale UB screening, supports efficient recycling and reuse operations, and provides a technological foundation for advancing second-life battery applications in energy storage and mobility sectors. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Rapid Capacity Diagnosis of Used Batteries Using Partial Discharge Data and Polynomial Modeling
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society
Journal of the Korean Solar Energy Society











